Let’s address the elephant in the room: keyword research is boring.
And if you’re new to this, it can be intimidating, frustrating, and borderline overwhelming.
So, here’s a checklist that will take all the guesswork out of what to do and when to do it as you research keywords.
Read on and simplify your keyword research now.
P.S. use this checklist with this template for a streamlined keyword research.
A Few Things to Prep Before Any Keyword Research
1. Clarify Your Business Goals
Before jumping into keyword research, take a moment to define your goals.
Do you want to:
→ Establish yourself as an industry leader?
→ Attract a new audience?
→ Drive more sales?
Clear objectives help you choose keywords that align with your overall vision.
2. Identify Your Target Audience
Don’t just guess who you’re talking to—really get to know them. Build audience personas, map out their entire journey, and understand their core problems. This way, when you pick your keywords, you’re not just throwing darts at a board, you’re zeroing in on what your ideal customers actually search for and need.
Let’s start by identifying your ideal customer profile (ICP). I’ll explain the process using a pest control service as an example.
Now, there are plenty of ways to identify your ideal customer profile, like doing market research by studying your local competitors. You can analyze their audience through website content, reviews, and social media engagement. By reading their reviews and feedback, you can pinpoint the exact pain points you can target.
For example, some people might be concerned about the high cost of pest control services or looking for eco-friendly and pet-safe solutions. Similarly, you might find complaints about slow response times or lack of availability in certain areas.
But there’s an easy starting point: ChatGPT!
Just give it a prompt like:
I have a [Your Business]. Create an ICP for a [Business Type] that I can use to do keyword research for SEO
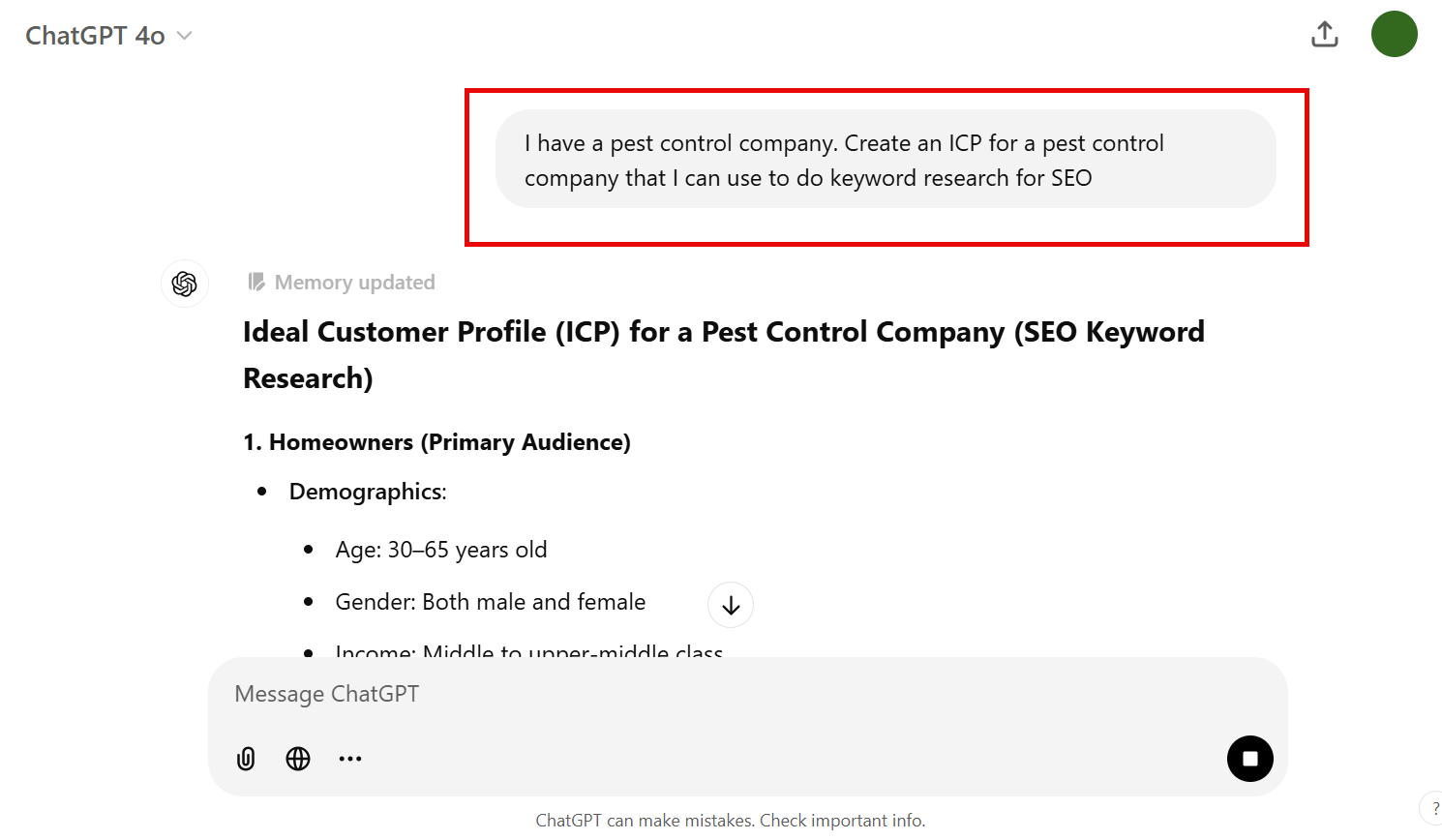
ChatGPT will give you details like your ICP’s demographics, like:
→ Their gender
→ Where they live
→ Their income level
→ Their interests and hobbies
→ The typical age of your customers
→ Their goals and needs from your service
→ Pain points related to your services: like the type of pests they get
You’ll also get a generic idea about their other concerns, like looking for eco-friendly and pet-safe solutions.
While this isn’t the most comprehensive approach, it’s a good place to get you started. Now, you have something you can expand on.
3. Understand Current Market Conditions
The online world doesn’t stand still, and neither should you. Stay on top of what’s trending in your industry, stalk your competitors (in a totally legal, non-creepy way), and pay attention to how seasons or events shake up search demand.
Doing this helps you pinpoint golden keyword opportunities before everyone else jumps on them.
Now that you have the basics out of the way, let’s dive into our step-by-step keyword research checklist.
10-Step Keyword Research Checklist
Here’s your go-to list of keyword research to kickstart your SEO content strategy:
1. Brainstorm a Seed Keyword List
The first step in your keyword research is to brainstorm a list of seed keywords.
Seed keywords are basically broad topics, terms, or phrases that define what your business is about– in other words, what someone might search to find your website.
These keywords can be related to your business as a whole, the product or service you offer, or your niche.
For example, if you run a pest control company, your basic seed keyword list should look something like this:
→ bed bug extermination
→ exterminator services
→ rodent removal
→ insect control
→ pest control
Now, these keywords will be a starting point for your keyword research. You can use them to expand your keyword list.
Here are a few ways to brainstorm a list of seed keywords for your business:
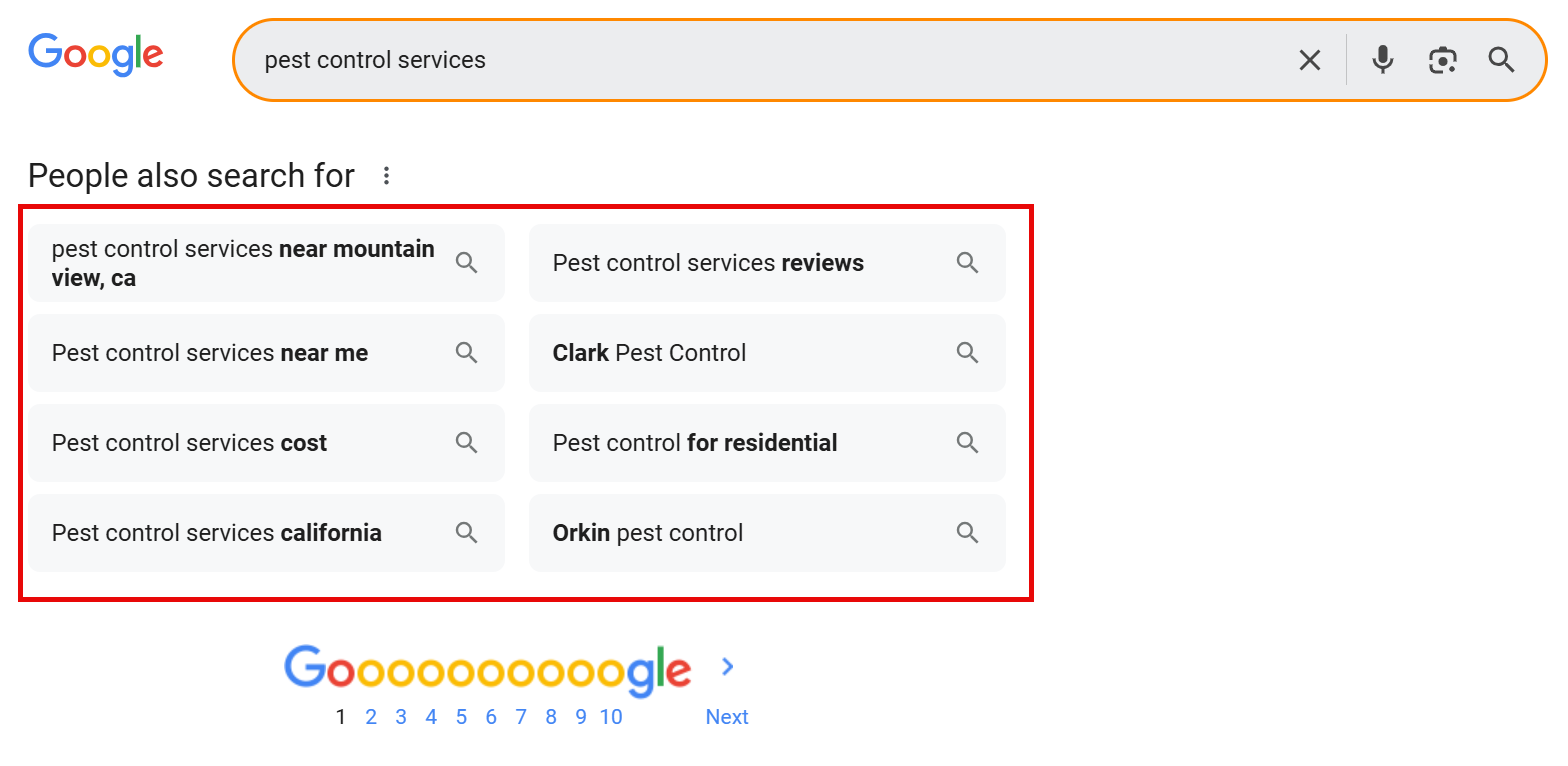
1. Google SERP Features: Use Google’s built-in features to start your keyword research. Start by typing in one of your seed keywords and look at the search results to see what ranks high. Look at the People Also Ask section to find what users are searching for.
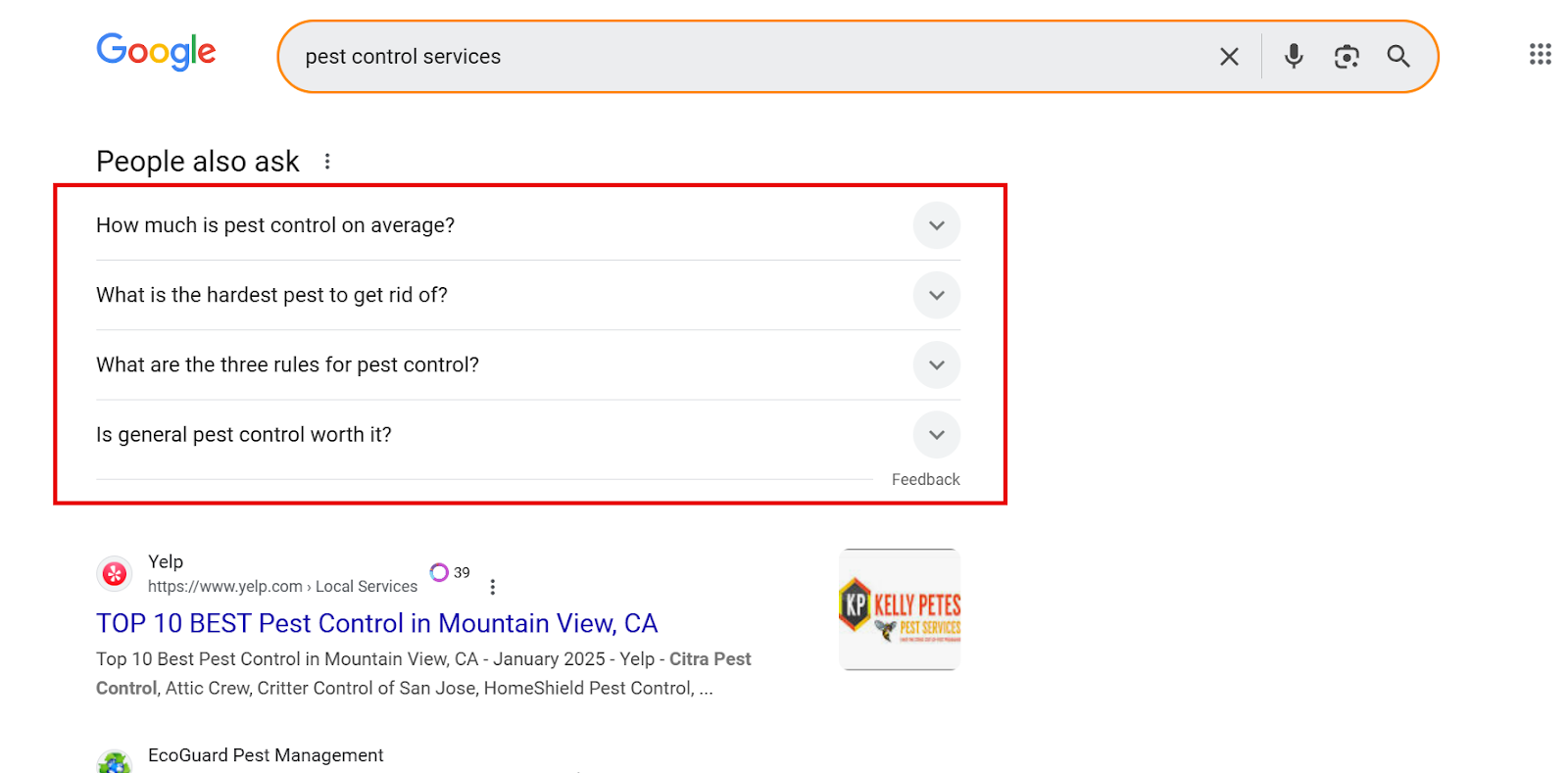
Scroll down the page to find the People also search for section. These related terms can give you ideas for more keywords.
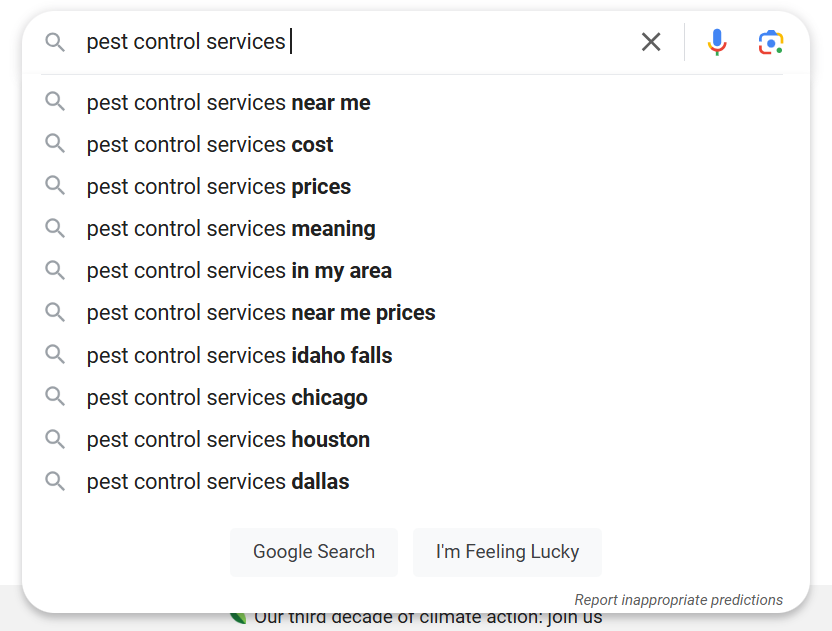
2. Google Autocomplete is another handy feature. Start typing your keyword, and watch for the suggestions that pop up. These often show what other people search for and can point you toward useful keyword variations.
3. Incognito Mode: For a “clean” look at results, use an incognito window. This way, you avoid personalized results and see what a typical user might see.
4. Google Trends is great for checking how interest in certain keywords changes over time. It can help you decide when to focus on certain topics.
5. ChatGPT is useful for brainstorming topics and finding related terms. Use it as a starting point, then double-check with real SEO tools.
2. Find Relevant Search Terms
After creating a list of seed keywords, find relevant search terms to expand your keywords list. There are a few ways to do it, like going through your competitor’s profile or running extensive Google searches to see what’s ranking.
But I prefer using SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool for this. It gives me plenty of keywords in one place along with valuable metrics.
Just enter one of your seed keywords into the Keyword Magic Tool, select your country, and click Search.
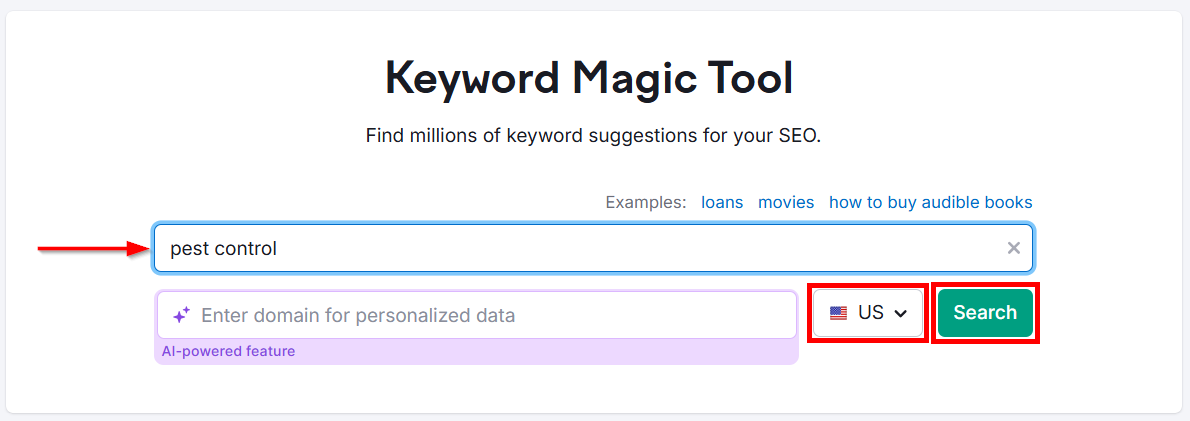
Now, you’ll see a list of thousands of keywords. Here’s what I do to narrow down this list to find keywords that are most relevant for my project:
- Select the types of keywords you want to see (like Questions, Broad Match, Phrase Match, Related, etc.)
- Try different filters like Volume, KD, etc. to find good volume keywords with easy keyword difficulty.
- Select the keywords you find relevant.
- Click the Export icon > Selected > XLSX.
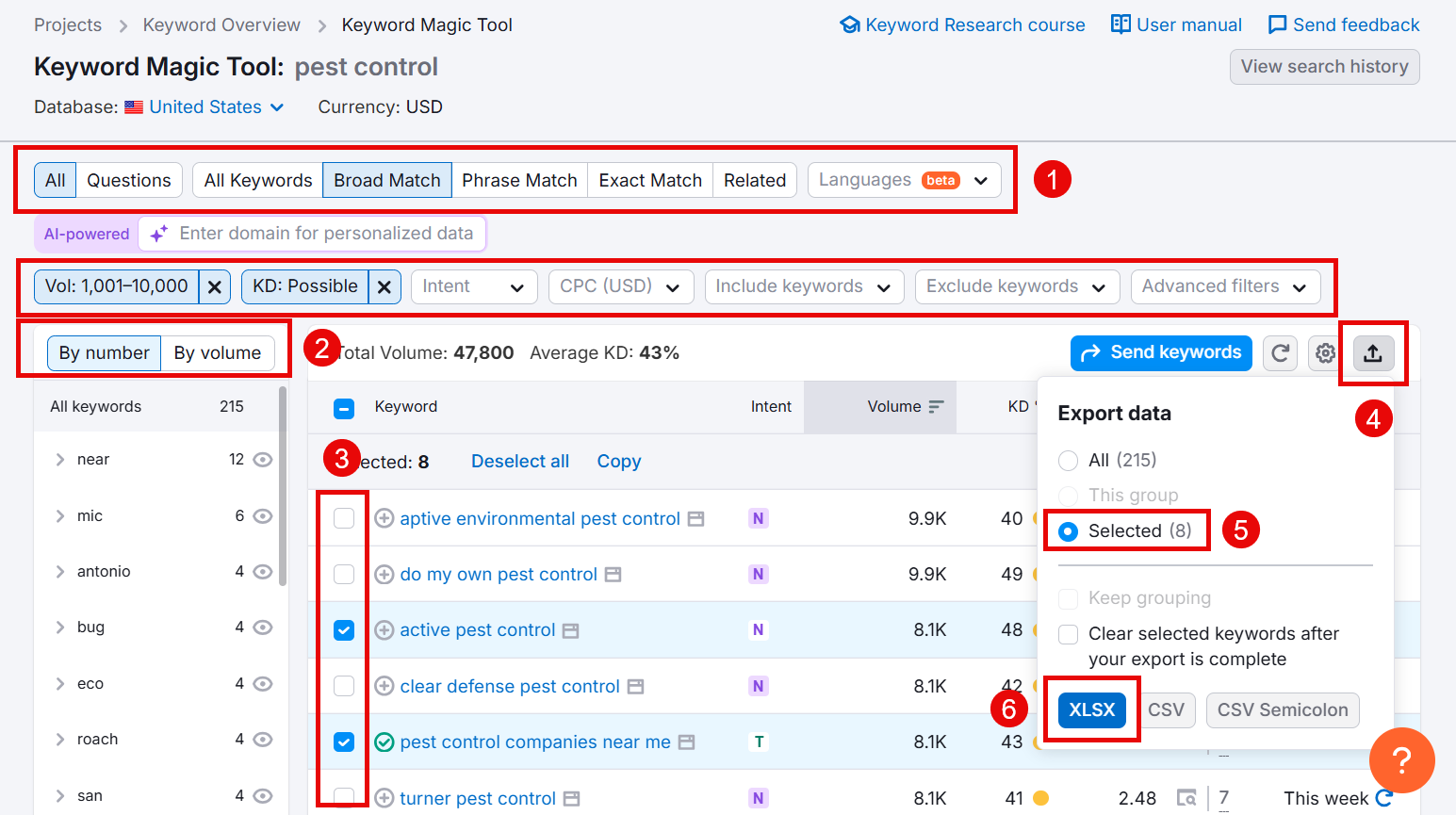
Follow the same steps for different seed keywords, and you’ll have a big list of important keywords and related search terms.
If you run a local business, add words that show where you’re located. For example, use your city or neighborhood name alongside your main keywords. So, for a pest control company located in New York City, it should be pest control company in New York City or pest control company in NYC.
If you’re targeting customers in different countries, research each place separately. Consider language differences, cultural habits, and the search engines people use in that part of the world (not everyone uses Google!). By customizing your keywords for each region, you’ll connect better with local audiences, making it more likely they’ll find your website and products.
3. Use Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are specific phrases or questions that target detailed searches.
They have a lower search volume and less competition because they’re more precise and less common. This means people searching for these terms are more likely to convert since they’re already interested in what you offer.
For example, a seed keyword like pest control may get thousands of monthly searches.
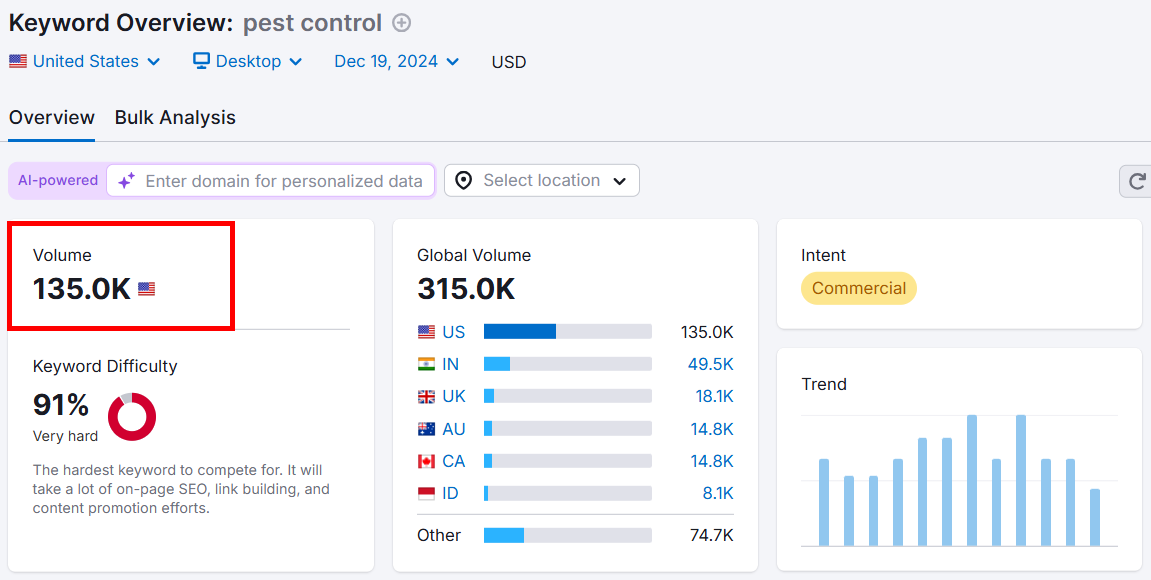
But if you search for a more long-tail phrase like pest control near me for mice, that will have a much lower search volume because it’s much more specific.
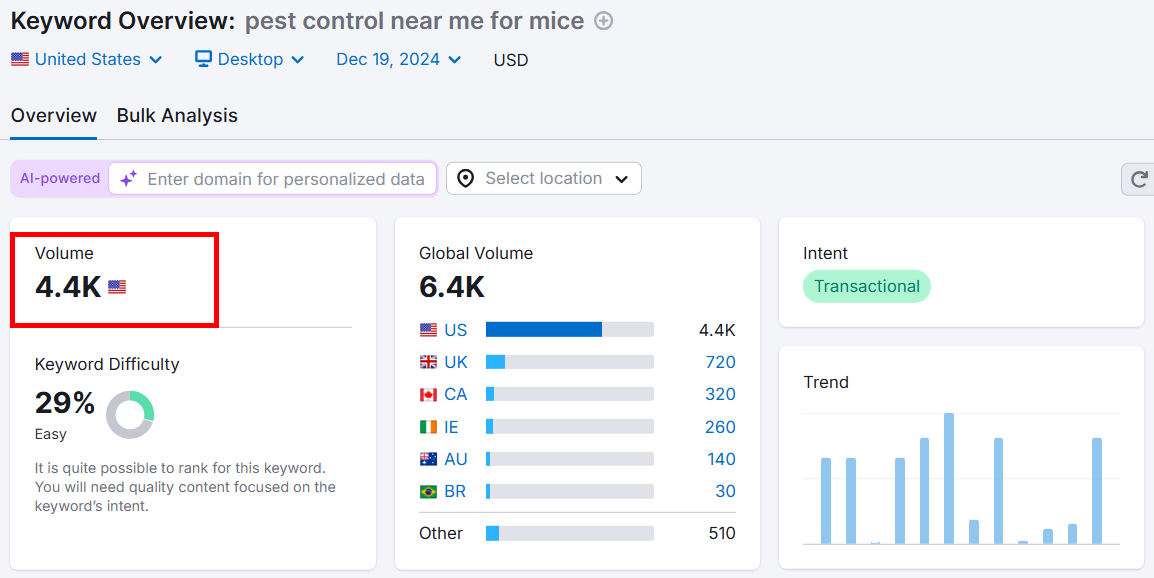
But someone searching for pest control near me for mice is closer to making a purchase than someone searching for pest control.
Once you understand your audience’s intent, create a list of long-tail keywords they might use to find solutions.
Plus, more and more people are using voice assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant to find what they need. Unlike typed searches, voice searches often sound more like everyday speech.
For example, instead of typing best coffee shop near me, someone might say: Where can I get a good cup of coffee around here?
To reach these users, include keywords that sound natural and conversational. Think about the common questions people might ask—who, what, where, how—and then shape your content to answer those questions in a friendly, helpful tone.
You can find long-tail keywords using different methods.
We already talked about how you can find keyword ideas using Google Autocomplete.
Another great place to look for long-tail keywords is online communities, like Quora, Reddit, and other forums. These communities are filled with real people sharing real problems—problems your content, products, or services can solve.
To find keywords, browse relevant forums or subreddits to spot common questions and pain points. Or use search operators on platforms like Reddit to focus on problem-related terms, like How to, I wish, or Where can I.
You can get good keyword ideas in these results. But if you want more, you can always find some related issues and questions in the comments.
If you’re looking for question keywords, like where can I find a good exterminator, I suggest using QuestionDB. It’s quick, easy, to the point, and free up to 5 searches a month.
You get a clear picture of questions peoples are searching for online related to your keyword.
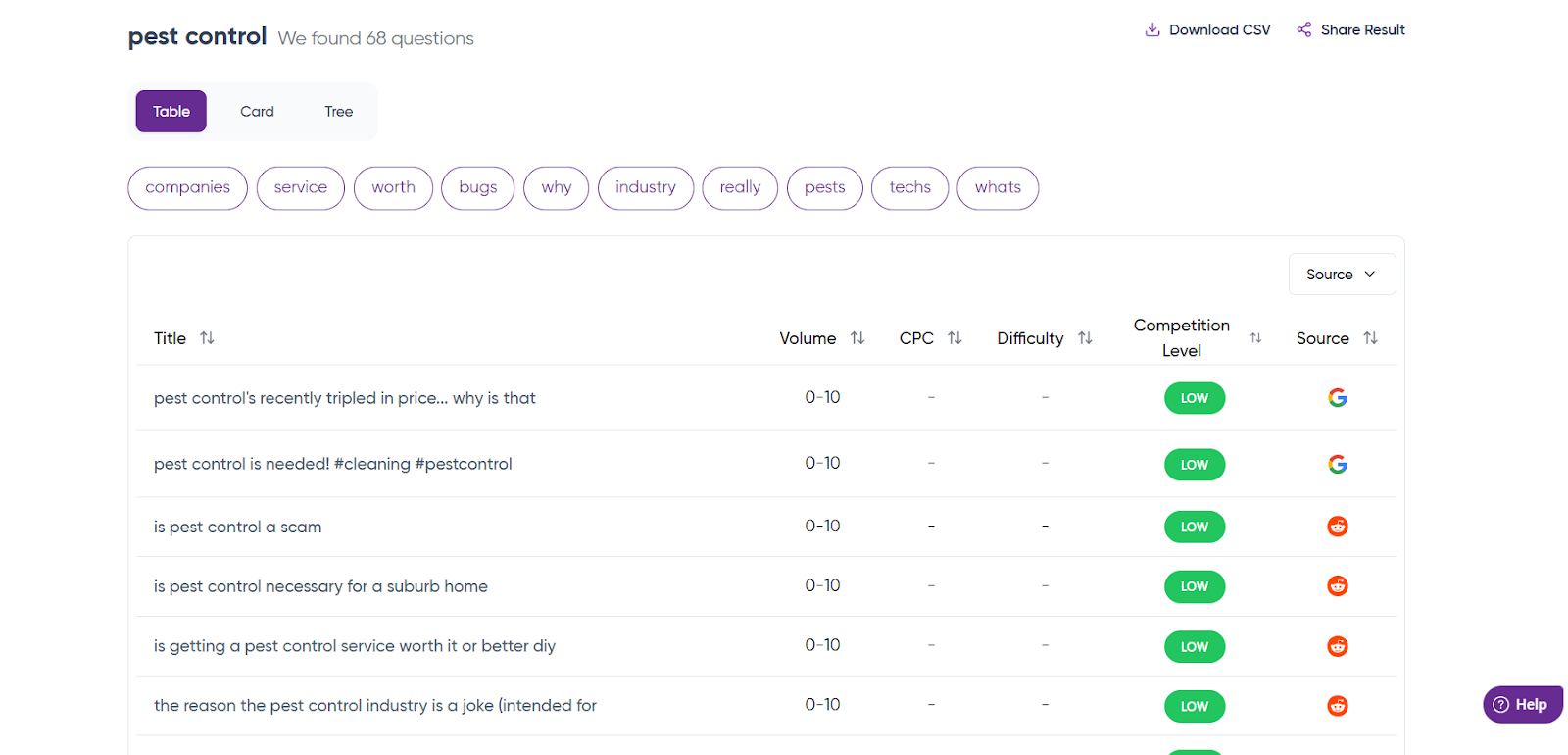
Once you get these questions, filter out the most promising ones and answer them in your content.
You can also use SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool to find question keywords using its Questions filter. Just go to the Keyword Magic Tool, type in your keyword, and select the Questions filter.
Now, you’ll get all question-based keyword results.
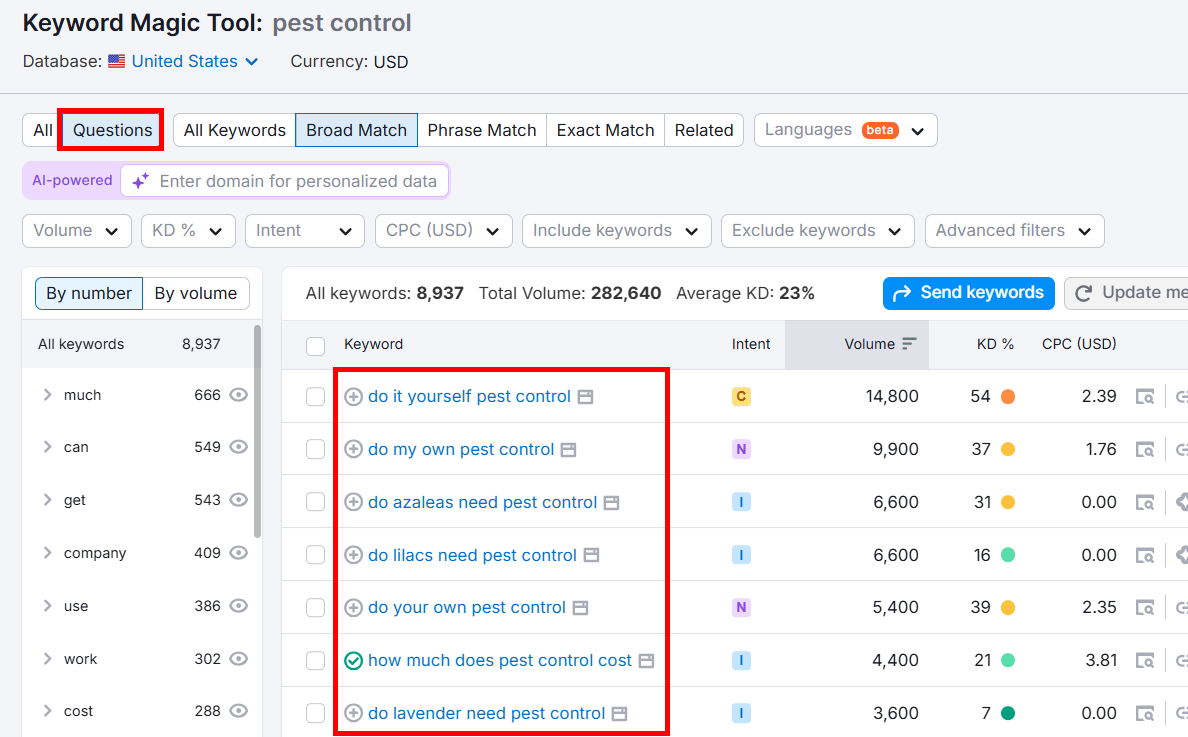
If you don’t want question keywords, click All.
Next, click the KD% option and select Easy.
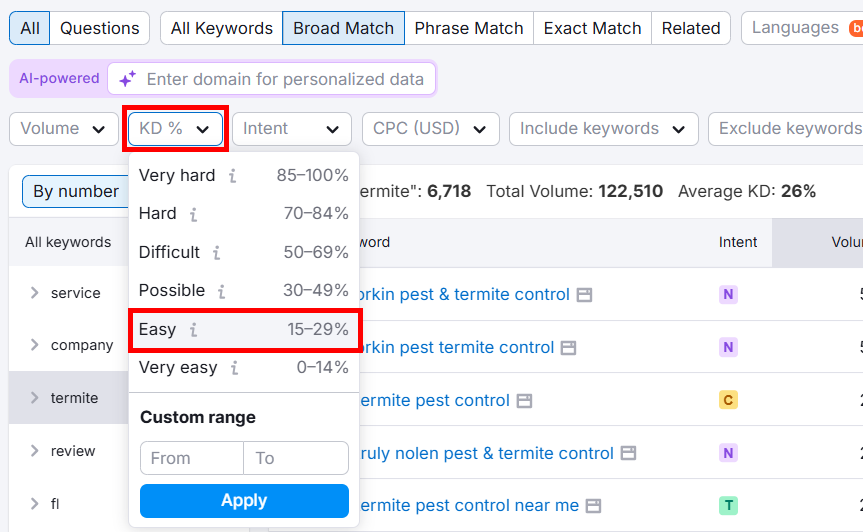
Now, you’ll get a list of mixed long-tail keywords.
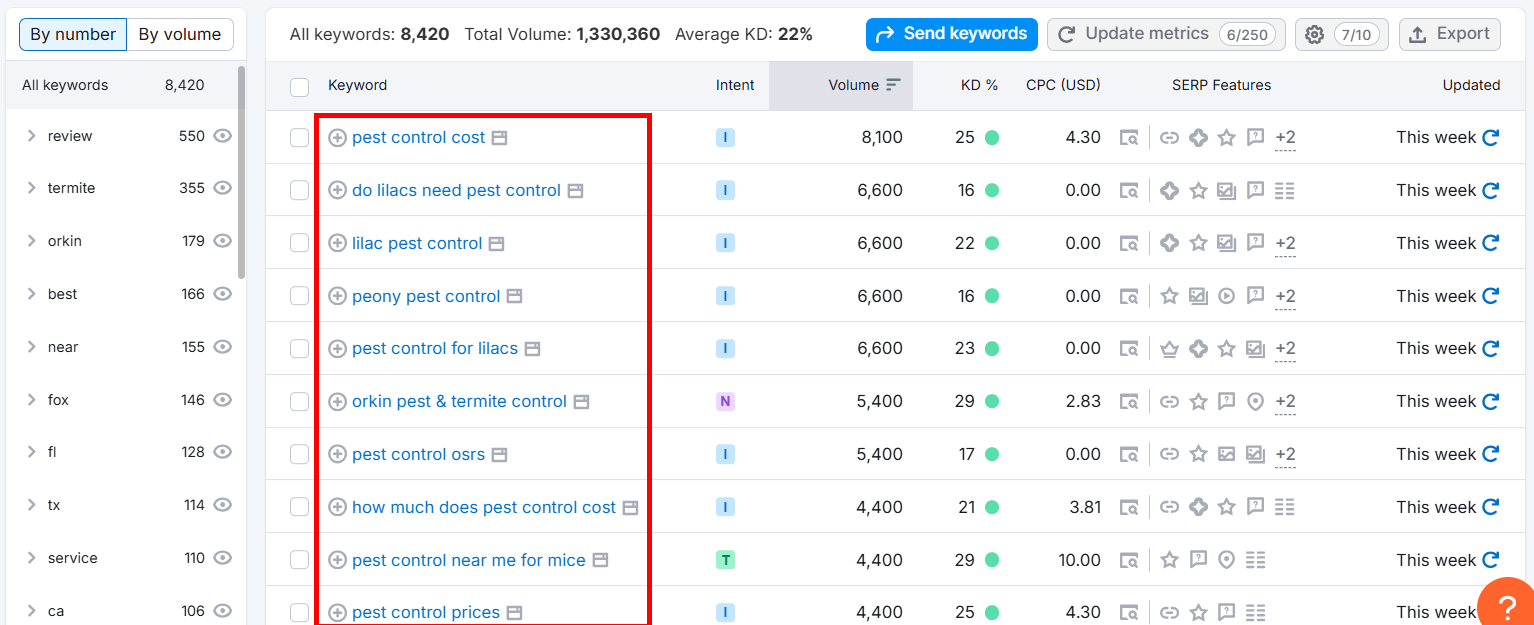
Keep repeating the same steps for different seed keywords and build a list of solid long-tail keywords.
4. Get Keyword Ideas From Competitors
Now, another way to get keyword ideas is to stalk your competitors.
But don’t get me wrong– I’m not talking about copying what they’re doing.
It’s about taking inspiration and making sure that you cover all relevant products/services/categories.
First, identify your competitors on Google. They are the ones that show up the most for your target keywords.
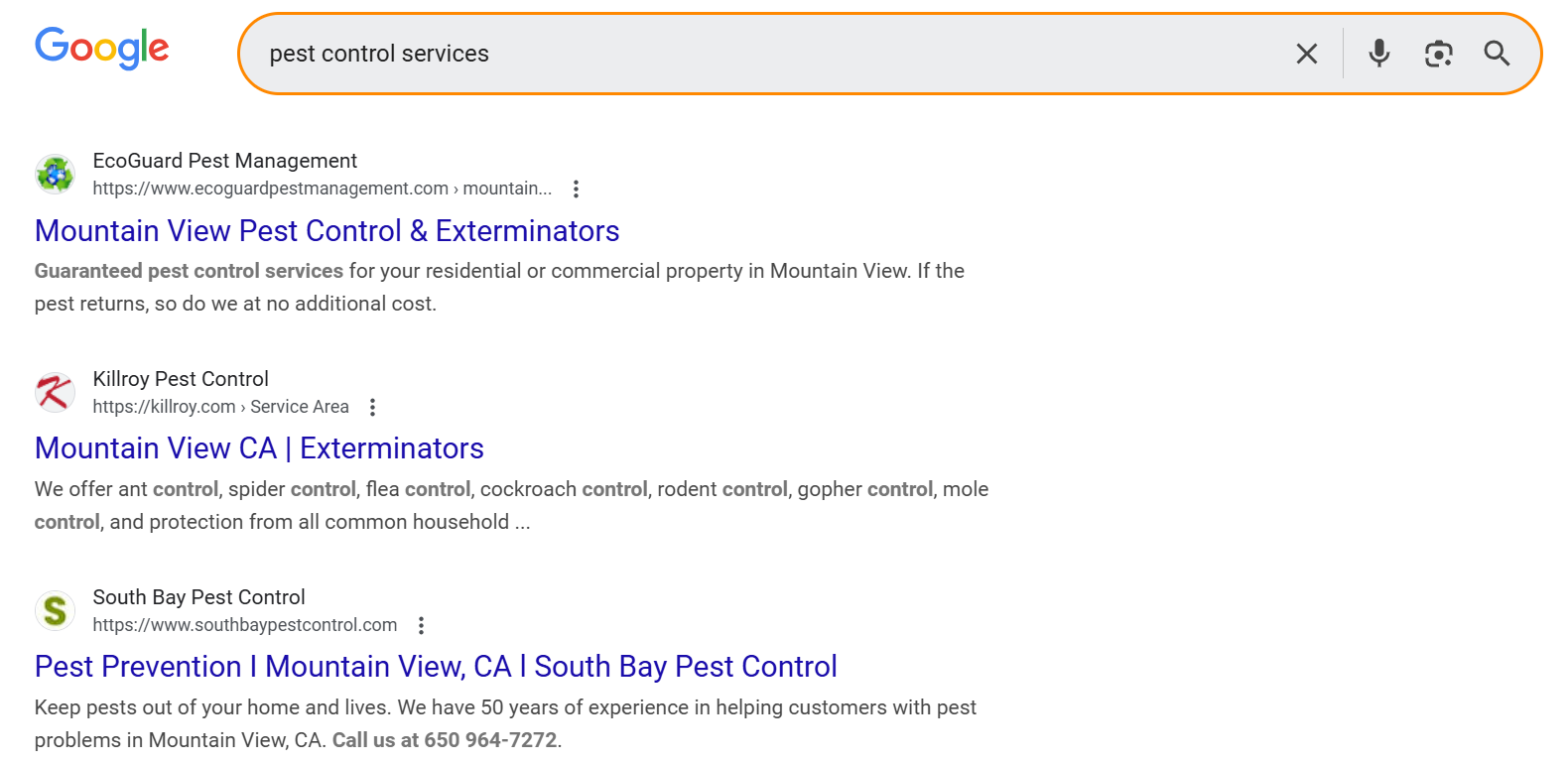
Analyze your competitor’s website to find keywords. Visit their blog posts, and other relevant pages. See what they are selling, how they categorize their products and services, and so on.
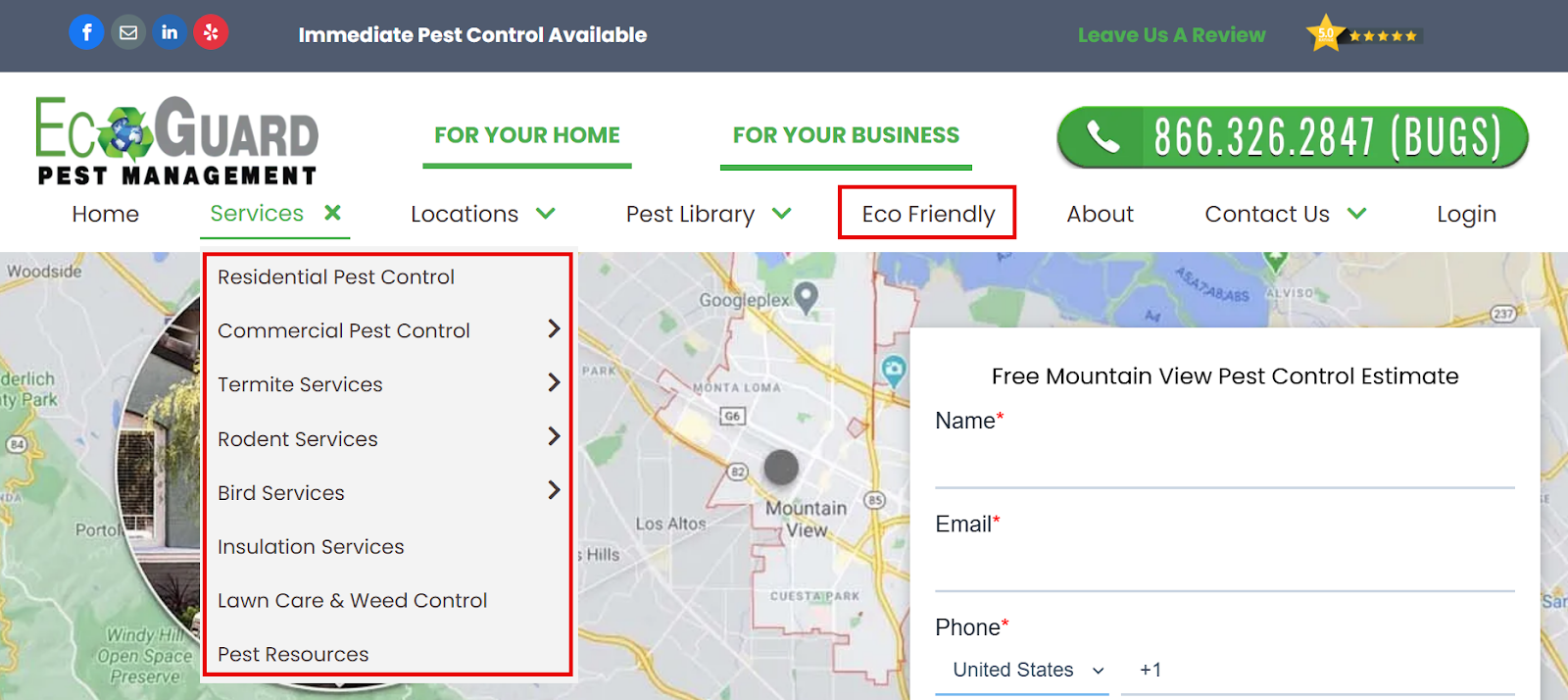
Pay attention to the keywords they use, the topics they cover, and the way they structure their articles.
Ask yourself:
↳ Are there keywords they’re ranking for that you’ve never tried?
↳ Do you have similar categories/products/services that they have listed but you haven’t listed them properly on your website?
By comparing their content to your own, you can spot places where you can offer something better—like more detailed guides, updated information, or a unique perspective that sets you apart.
For an in-depth keyword gap analysis, use SEMrush Keyword Gap tool. It’s just easier and more accurate.
Go to the Keyword Gap tool in Semrush.
Enter your URL along with four of your competitors’ URLs and click Compare.
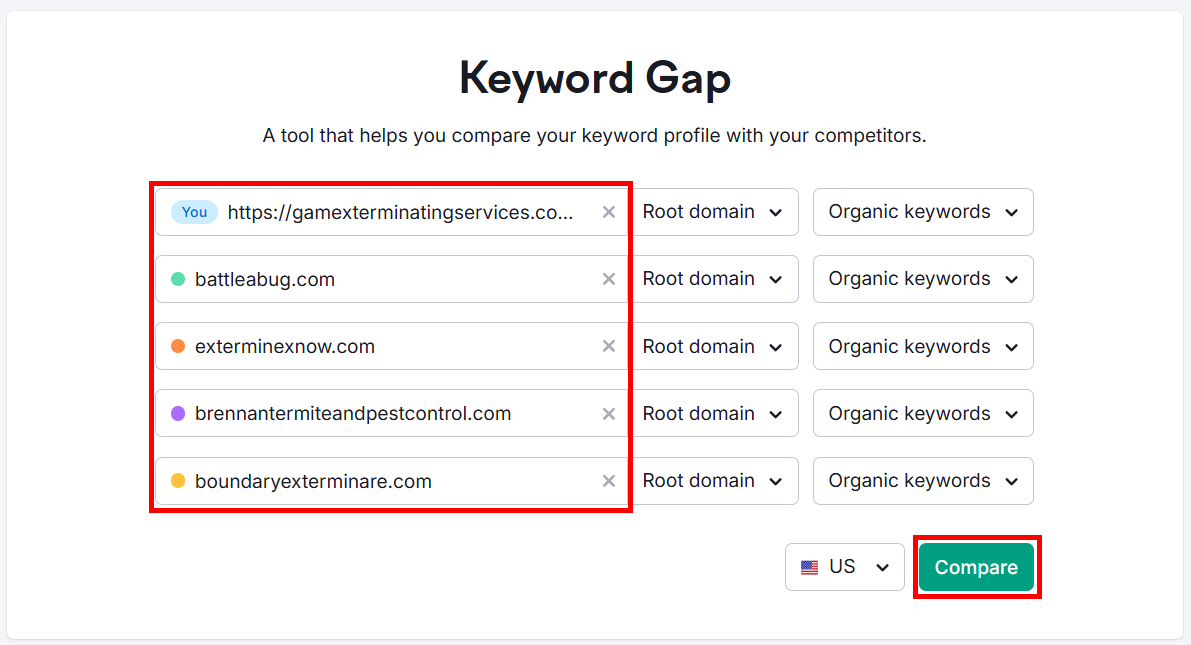
Scroll down to the table and click the Untapped tab to see all the keywords your competitors are ranking for, but you’re not.
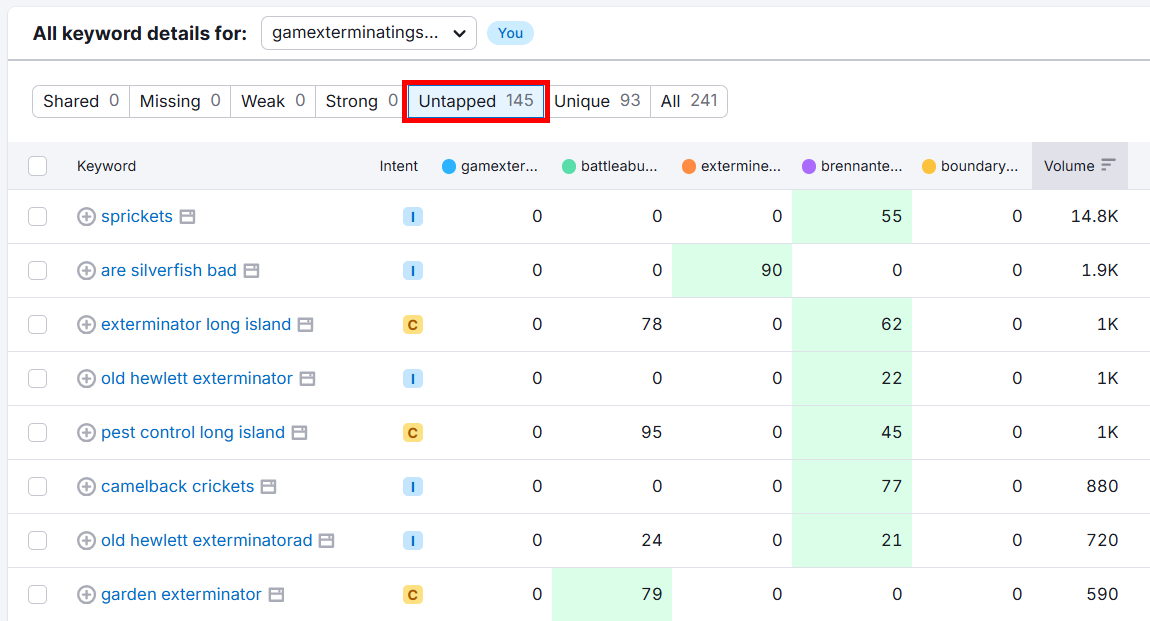
Many of these keywords can be great opportunities for you to target.
5. Analyze Search Intent
When someone types a query into Google, they’re not just looking for words—they have a reason behind their search. This reason is called “search intent”.
Why is search intent such a big deal? Because Google’s main goal is to give people exactly what they’re looking for.
If you understand what your ideal customer intends to find, you can create content that hits the mark. This makes it far more likely that your pages will rank well and attract the right visitors.
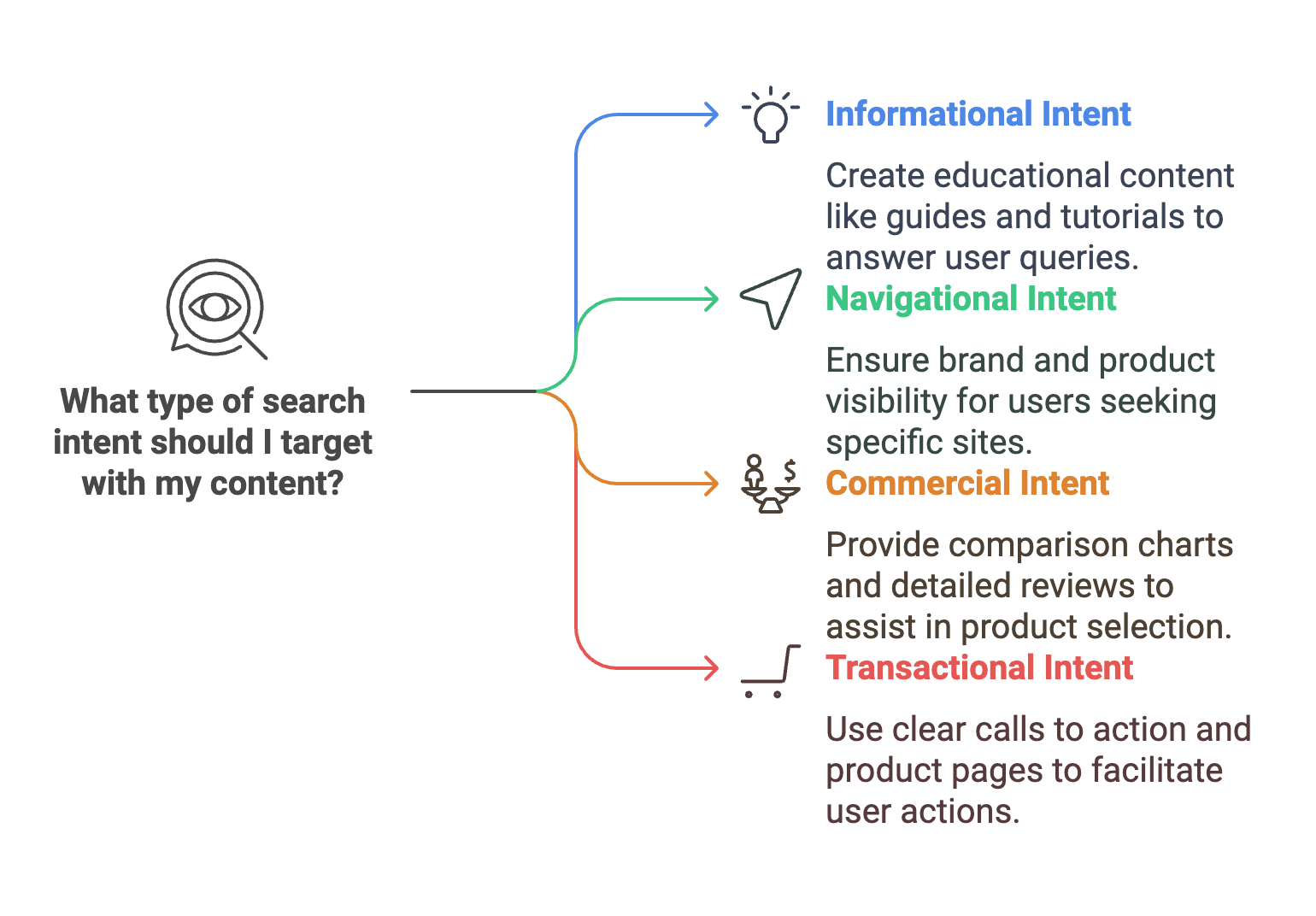
There are four main types of search intent:
↳ Informational: The user wants to learn something or find an answer. These queries often start with how, what, why, or, when. They might ask “how to start a blog” or “what is keyword research?” In this case, guides, tutorials, and educational articles work best.
↳ Navigational: The user is trying to reach a specific site or page, like “SEMrush login” or “Amazon customer service.” Your job here is to make sure your brand and products are easy to find if someone’s already looking for you.
↳ Commercial: The user is considering a purchase and wants to compare products or services. For queries like “best coffee shops in town” or “top pest control services,” think comparison charts, product lists, and detailed reviews.
↳ Transactional: The user is ready to take action—buying something, signing up, or downloading a tool. For example, “buy SEMrush subscription” or “hire a rodent exterminator” shows they’re ready to commit. Clear calls to action, product pages, and checkout options are key here.
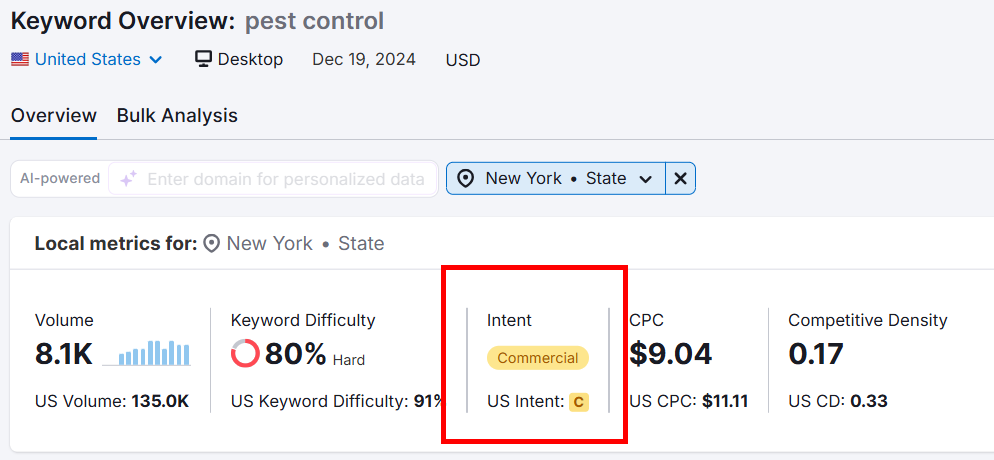
If you’re not sure how to find search intent, I suggest using the SEMrush Keyword Overview as it clearly shows search intent with each keyword.
Just enter your keywords (you can add up to a 100 to analyze them in bulk) and you’ll see the search intent like this:
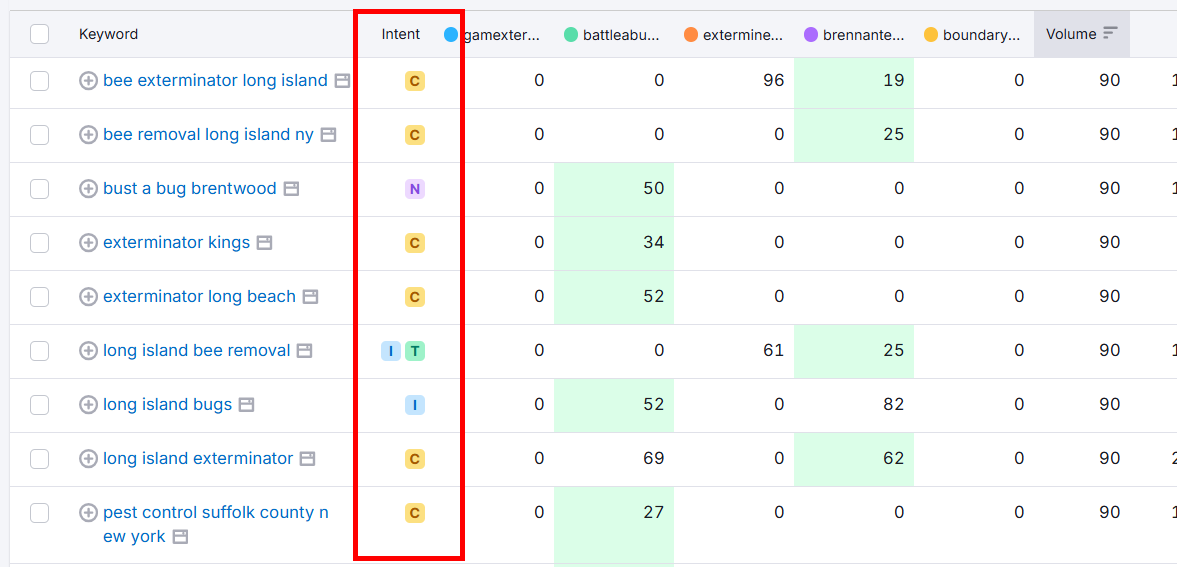
You can also check the Intent column in your active keyword research windows.
You can also use the Intent filter to focus only on the type of intent you want—like choosing all transactional keywords if you’re creating a sales page.
Once you know the intent behind each keyword, you can plan your content accordingly.
6. Check Important Keyword Metrics
By now, you should have a long list of potential target keywords. But not all keywords are worth targeting.
Some are too competitive to rank for. Others won’t bring much traffic or lead to conversions.
So, how to avoid targeting keywords fruitlessly?
Analyze each keyword’s metrics before deciding which ones to focus on.
Using SEMrush’s Keyword Overview tool (like we did in the last step) can help you quickly check valuable metrics for up to 100 keywords at a time. Focus on details like:
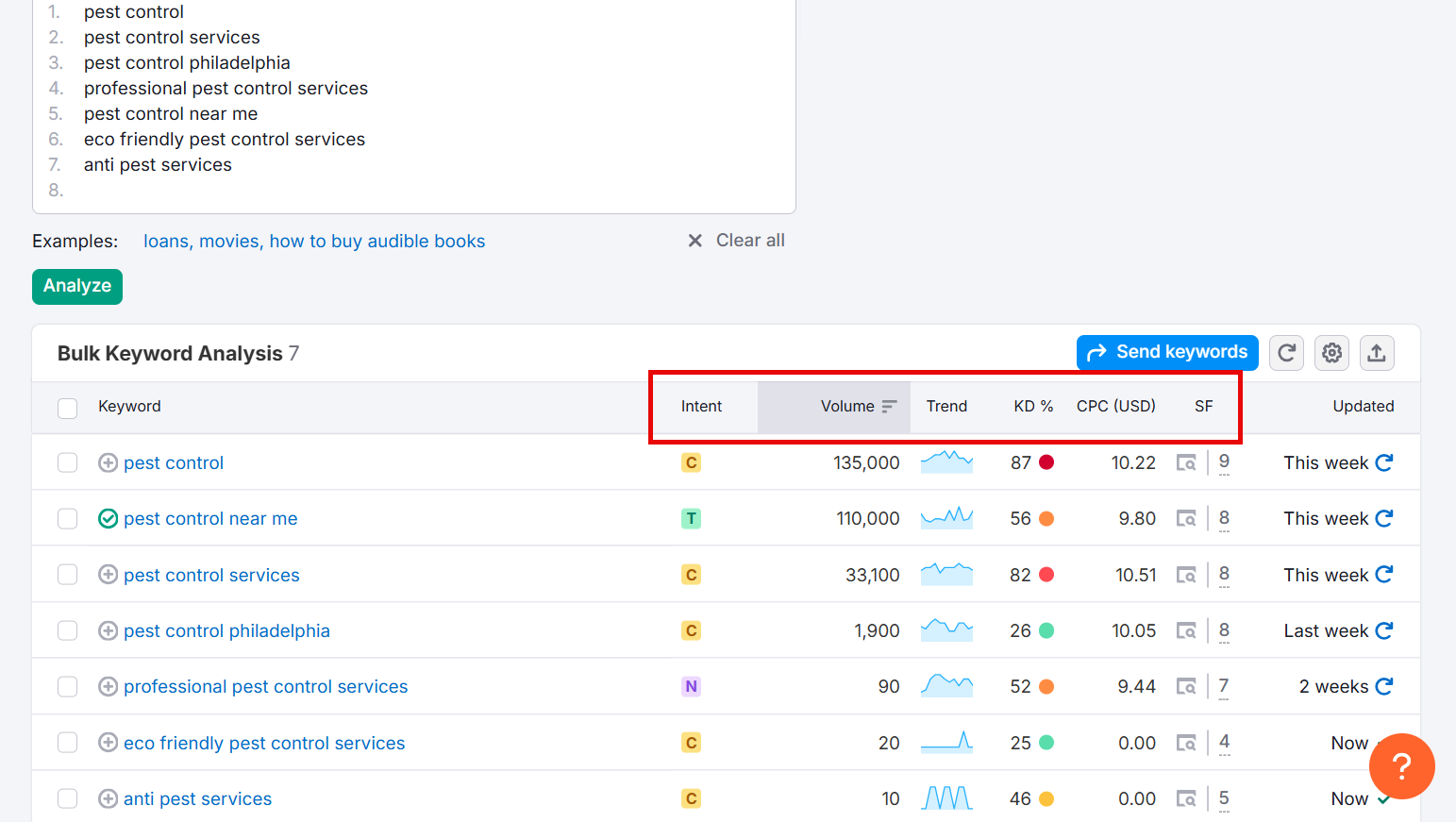
→ Search volume: How many times, on average, people type this keyword into Google each month.
→ Keyword difficulty: An estimate of how tough it might be to rank on the first page for that keyword.
→ CPC (Cost Per Click): How much advertisers are willing to pay each time someone clicks on an ad triggered by that keyword.
→ SERP features: Special results that appear on the search page (like featured snippets, image packs, or FAQs).
A general rule of thumb: Pick keywords with low difficulty and high search volume.
P.S. check out this post to learn what a good keyword search volume for your business, in relation to other metrics and factors.
By focusing on these metrics, you can refine your list and zero in on realistic, high-potential keywords for your SEO strategy.
7. Cluster Your Keywords
Now that you have your keywords, what to do next?
First, organize your main keyword list into clusters based on related topics, themes, or user intent.
Group them under your pillar topic for a more structured approach. Your primary keyword represents the main topic you want to rank for, while secondary keywords support and expand on it.
For example, for a pest control company:
↳ Primary keyword: pest control services
↳ Secondary keywords: affordable pest control near me and eco-friendly pest control solutions
Organizing these keywords into clusters lets you create content that ranks for multiple search terms while addressing a variety of user needs.
You can use SEMrush’s Keyword Strategy Builder for keyword clustering.
Open a keyword list you’ve already created or click create a regular list to import your keywords from a spreadsheet. Then, click Create list.
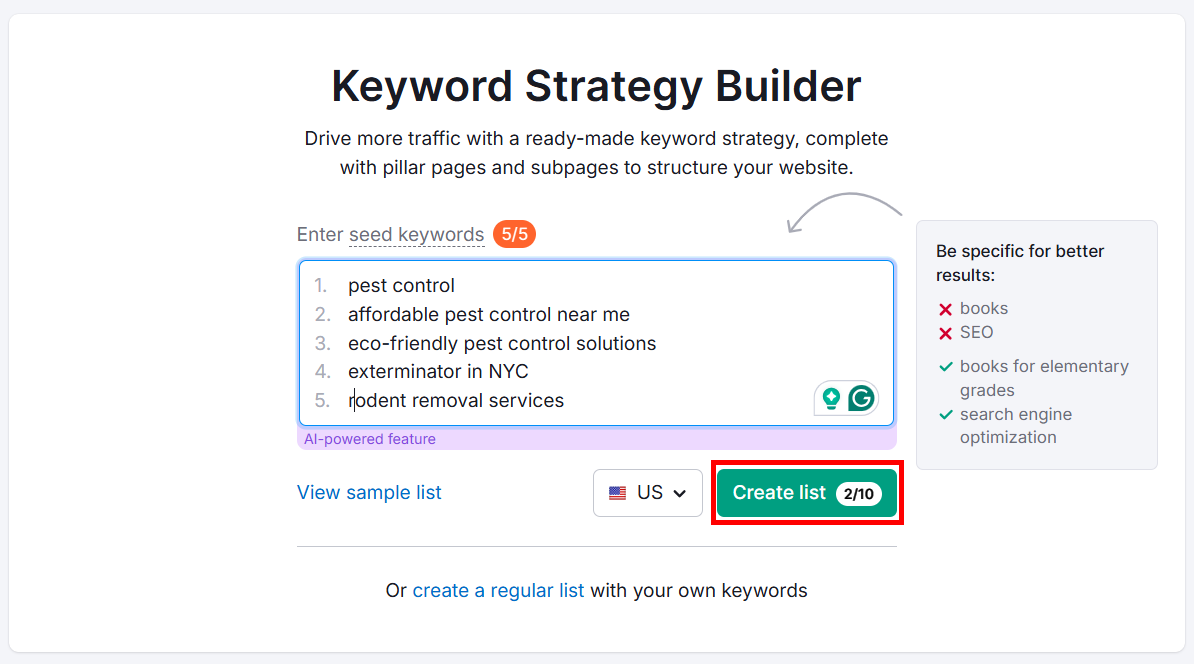
You’ll see all related keywords automatically grouped based on their intent.
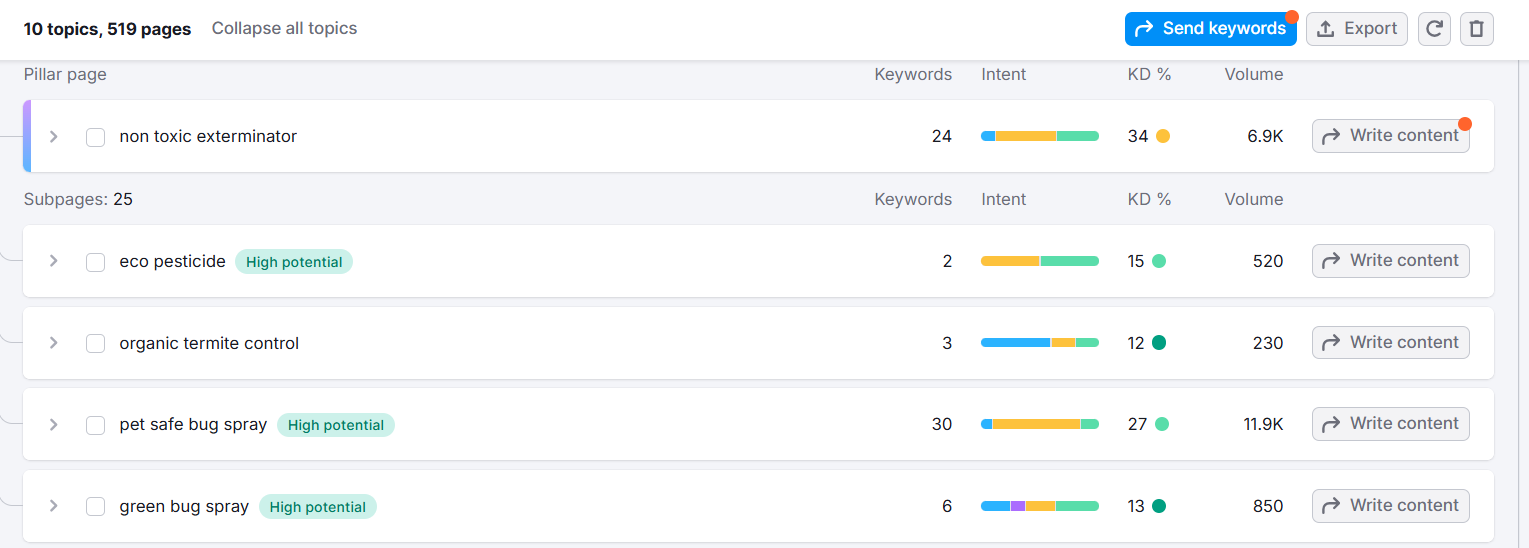
If you want to see all the keywords in a cluster with their metrics, click the little arrow next to it, and it will show you a list of secondary keywords, like this:
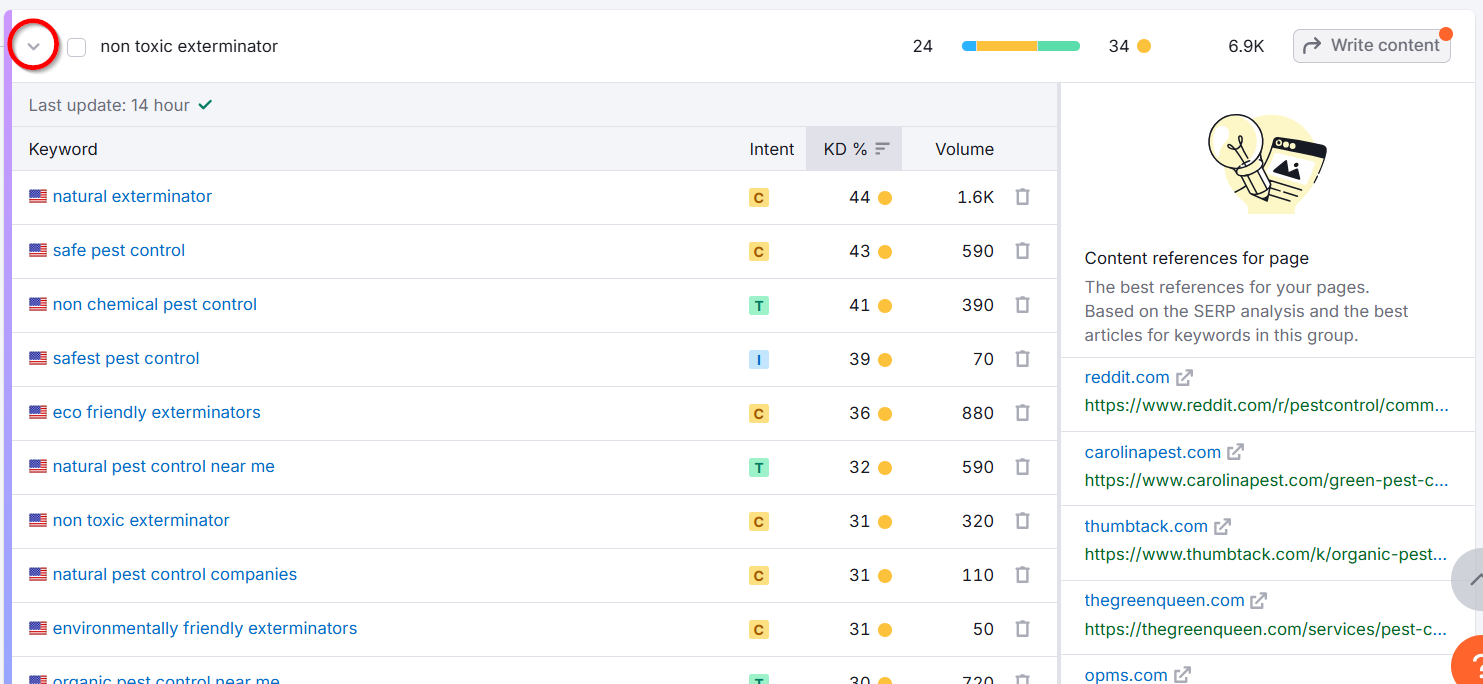
Use these clusters for keyword mapping—assigning keywords to specific pages on your site.
This helps you optimize pages for the right keywords, avoid keyword cannibalization, and find and fill content gaps.
8. Prioritize Your Keywords
To prioritize keywords, you can segment keywords by funnel stage.
↳ Top-of-Funnel (ToFu): High search volume, awareness-stage keywords like what is pest control. Great for attracting new visitors.
↳ Middle-of-Funnel (MoFu): Moderate volume, consideration-stage keywords like best pest control services. Perfect for nurturing leads.
↳ Bottom-of-Funnel (BoFu): Low volume, high-intent keywords like pest control service near me. Perfect for driving sales.
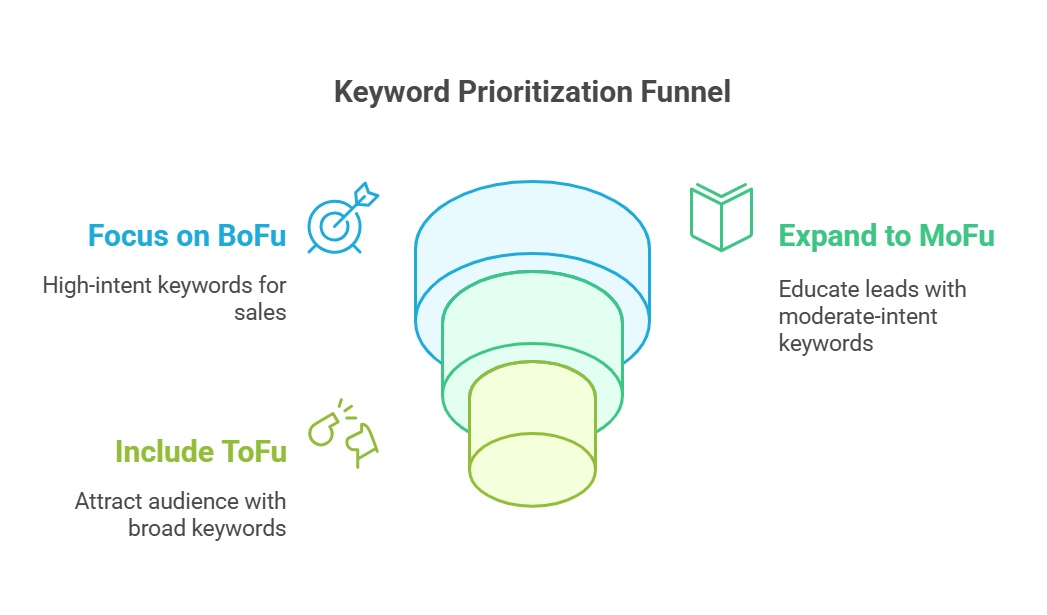
You should start with BoFu keywords and focus on high-intent keywords aligned with your core services to drive sales and revenue quickly. Then, expand to MoFu keywords to educate leads about your value and solutions. Lastly, include ToFu keywords to attract a broader audience and build brand awareness.
Create a spreadsheet of your top 10-20 keywords that you want to focus primarily on your website.
For example, you might pick keywords like the following for a pest control company:
→ best pest control companies in NYC
→ pest control services in NYC
→ how to remove termites
→ exterminator near me
9. Finalize Your Keyword List
Now that you have completed all the above steps, you should have a long list of keywords and phrases that you’ll use in your website content.
You should have:
↳ 1 primary keyword with low difficulty and high volume
↳ A long list of secondary keywords related to your primary keyword
Now it’s time to put your keywords to use.
Decide where each keyword fits best on your site:
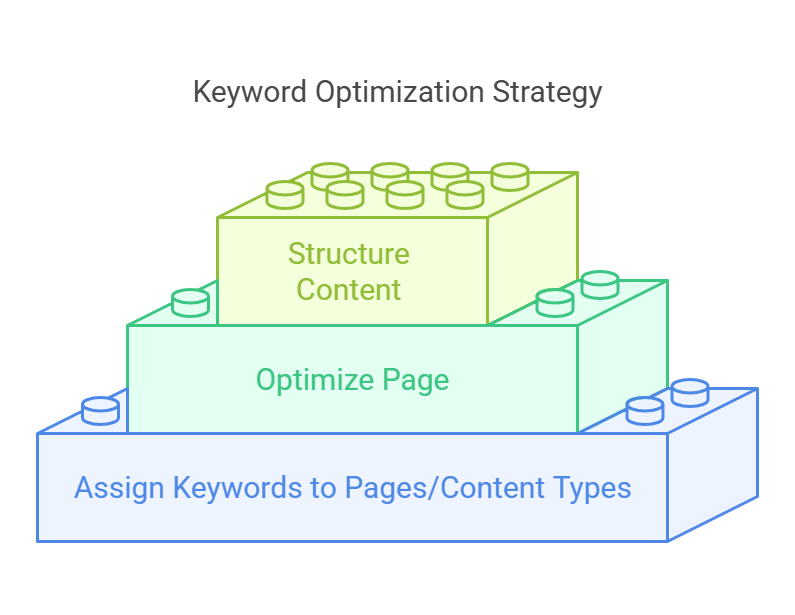
→ Product pages: Focus on keywords with clear buying intent.
→ Blog posts: Use keywords suited for informative or how-to content.
→ Pillar pages: Target broad keywords for in-depth coverage of a topic.
→ Resource hubs: Combine related keywords to create comprehensive guides.
By organizing keywords logically, you make it easier for users and search engines to understand your site’s structure and value.
Once your keywords are assigned, optimize your pages with clear, engaging titles and meta descriptions that include primary and related keywords. Use headings (H1, H2, H3) to structure your content for readability and better search engine understanding.
10. Track Your Positioning
Once your keyword strategy is in place, it’s important to keep an eye on how it’s performing. Look out for these key metrics:

↳ Organic traffic: Tracks how many people find your site through search engines. A steady increase shows your keywords and content are working.
↳ Keyword rankings: Check where your pages rank for target keywords. Higher rankings mean more potential visitors.
↳ Click-through rates (CTR): Measures how many searchers click your page. A high CTR means your titles and descriptions attract attention.
↳ Engagement signals: See how long visitors stay, how many pages they view, and if they quickly leave. Positive signals mean your content meets their needs.
↳ Conversions: Track actions like sign-ups, purchases, or form submissions. Conversions show your keywords are bringing the right audience.
↳ Brand visibility: Compare how often your brand appears in search results versus competitors. More visibility builds trust and recognition.
Monitoring and tracking your position is essential for good SEO. I suggest using Google Search Console to do this.
Check Off All Your Keyword Research Tasks
And there you have it! Now you know how to do keyword research for your e-commerce store, SaaS website, blog or even a YouTube channel!
Just follow the steps I laid out above, and you should have a solid SEO strategy for your business.
Keep an eye on your rankings over time. If a keyword slips in position, refresh your content or try a new angle. Test different keyword placements, headings, and page structures to see what drives better results.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Find Topics – Identify broad topics relevant to your business.
2. Generate Keywords – Use tools like Google Keyword Planner to get keyword ideas.
3. Analyze Competition – Check keyword difficulty (KD) and competitor rankings.
4. Check Search Intent – Ensure the keyword matches user intent.
5. Prioritize and Use – Pick high-value keywords and optimize your content.
List keywords by categories (topics, long-tail, short-tail), search intent (informational, transactional), and priority (high, medium, low competition). Use keyword research tools to collect data, then organize them in a spreadsheet with metrics like search volume, keyword difficulty (KD), and ranking potential.
Here’s an overall checklist for SEO in 2025:
☑ Google Business Profile – Fully optimized with updated info.
☑ Local Keywords – Use city/state-specific terms.
☑ NAP Consistency – Name, address, phone must match everywhere.
☑ Local Citations – Get listed on directories.
☑ Reviews – Encourage and respond to customer feedback.
☑ Mobile-Friendly Website – Ensure fast load times.
☑ Localized Content – Write blog posts on local topics.
Broadly, these are the 3 main steps of keyword research:
1. Find Seed Keywords – Identify main keywords related to your business.
2. Expand & Analyze – Use tools like Ahrefs or SEMrush to get variations and check competition.
3. Select & Optimize – Choose the best keywords and use them in your content, meta tags, and URLs.
Use Google Search Console to see what keywords your site ranks for. Check Google Analytics for traffic sources. Use SEO tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest to analyze rankings, search volume, and competition. Manually search on Google to check how your content appears.
Read the main topic and highlight important terms. Look for recurring words in research papers, books, or articles. Use mind maps to break complex ideas into smaller parts. Tools like Google Scholar or academic databases help find related keywords and key concepts.
Use AI-powered tools like ChatGPT, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to generate ideas quickly. Check Google Autocomplete and People Also Ask for quick insights. Analyze competitors’ keywords using SEO tools. Filter results by search volume, keyword difficulty, and intent to find the best options.
KD (Keyword Difficulty) shows how hard it is to rank for a keyword. It’s based on competitor strength, backlinks, and content quality. A lower KD means an easier chance to rank. Tools like Ahrefs and SEMrush provide a KD score to help prioritize keywords.
Use Google Autocomplete, People Also Ask, and Keyword Planner for quick insights. Analyze competitors’ top-ranking pages with Ahrefs/SEMrush. Use AI-powered tools like ChatGPT for fast topic expansion. Focus on low-competition, high-intent keywords to get quick wins.
Find words that describe your topic. Use Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, or SEMrush to get keyword ideas. Check competitors’ content for recurring terms. Look at Google Autocomplete and Related Searches for variations. Prioritize keywords based on search volume and difficulty.
Brainstorm main topics relevant to your business. Use keyword tools to find variations. Organize keywords by search intent (informational, navigational, transactional). Group them based on difficulty and volume. Store them in a spreadsheet for easy tracking and prioritization.
