Your competitors are showing up in local searches, bringing in customers who could’ve been yours.
Why? Because they’ve cracked local keyword research—and you haven’t.
The right local keywords help you rank where it matters most: in front of customers who are ready to buy in your city, neighborhood, or street.
Get this right, and you don’t just rank—you dominate.
In this guide, I will show you EXACTLY how to do it.
Free Local Keyword Research Template For Small Businesses
Get my Free Small Business Local Keyword Research Template and fill it with keywords as you follow the guide.
📌 Local Keyword Research Checklist
Identify Your Core Services & Locations
- List all products/services you offer.
- Specify the cities, neighborhoods, or areas you want to target.
Brainstorm & Research Seed Keywords
- Write down general terms your customers might search for.
- Use Google Autocomplete, People Also Ask, and Related Searches for ideas.
- Analyze competitors’ websites for commonly used terms.
- Use keyword tools (SEMrush, Ahrefs, Google Keyword Planner) to find search volume and difficulty.
Add Local Modifiers
- Include city names, neighborhood names, landmarks, and zip codes.
- Find implicit keywords (e.g., “car wash near me”).
Analyze & Prioritize Keywords
- Check search intent (informational, commercial, transactional).
- Assess search volume and keyword difficulty (choose low-competition, high-relevance terms).
Map Keywords to Specific Pages
- Assign each keyword to a relevant page (or plan new pages).
- Prevent keyword cannibalization (don’t target the same keyword on multiple pages).
Optimize Google Business Profile with Keywords (GBP)
- Use relevant local keywords in the business description.
- Ensure NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) consistency across platforms.
- Add geo-tagged images with keyword-rich filenames.
- Update content using target keywords.
Step-By-Step Keyword Research Guide For Small Businesses
1. List What You Offer and Where You Offer It
Start by identifying the what of your business– or in other words your core services. Write down all your products or services and the specific locations you want to target.
Here are a few ways to do it:
a. Brainstorm Your Seed Keywords
Seed keywords basically define what your business offers. They are short, generic phrases most relevant to your business. For example, car wash is the most common seed keyword for a car wash service.
You can use these keywords to find more specific, related phrases like “car detailing near me.”
Start by brainstorming a list of core terms based on what you know about your business. Note them down in a spreadsheet. If you’re doing it for a client, ask to all list the services they offer.
Here’s how to create a list of seed keywords for your local car wash business:
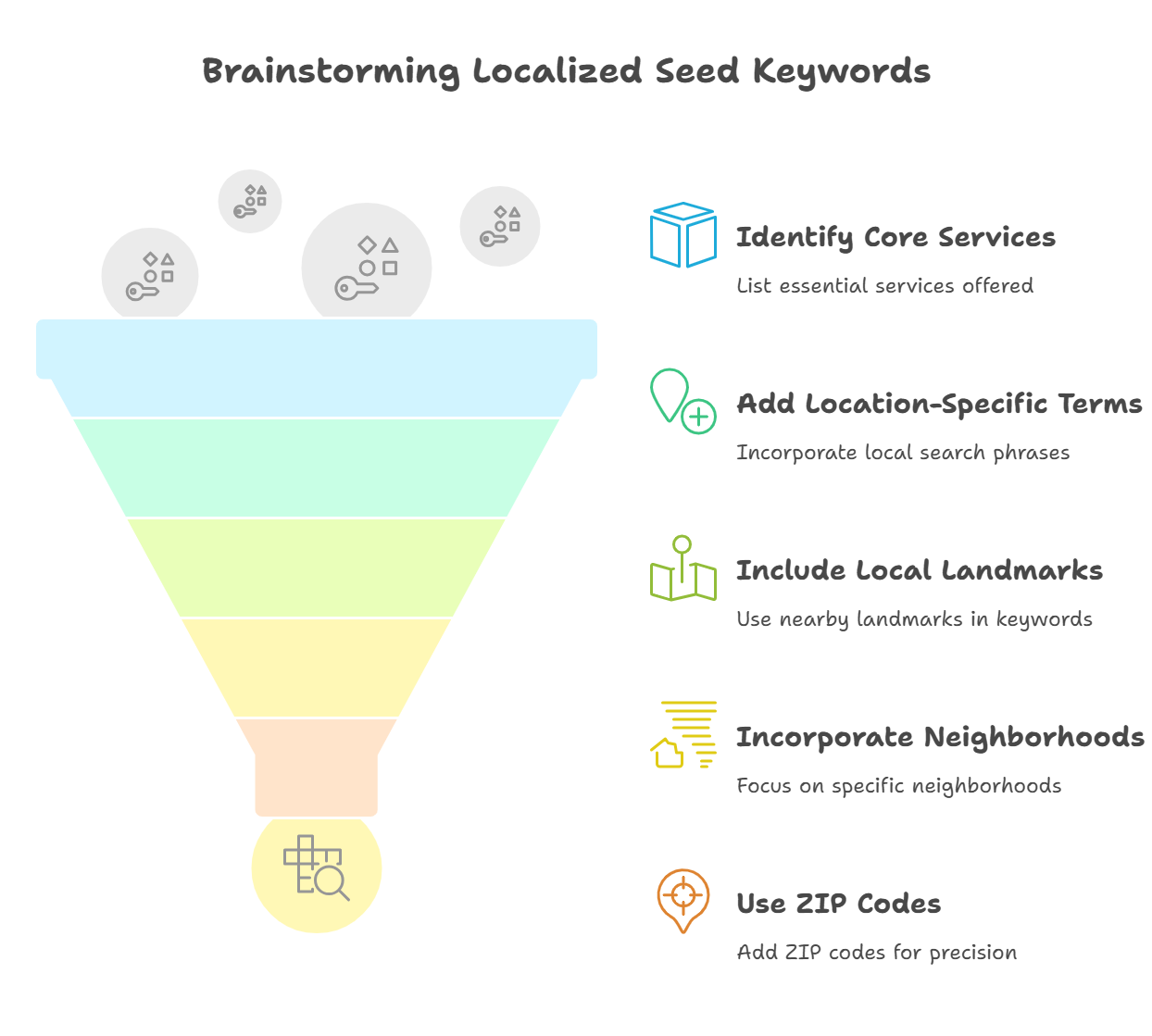
Start with general terms that customers might search for when looking for your services, without considering location. For example:
→ car wash
→ auto detailing
→ car cleaning
→ car waxing
Add location-specific terms that people might use to find a car wash in your area. For example:
→ car wash in California
→ car detailing near Los Angeles
→ car wash in Bay Area
People often include local details in their searches, such as:
→ Landmarks: car wash near Griffith Park
→ Street names: car wash on Sunset Boulevard
→ Neighborhoods: car detailing in Beverly Hills
→ ZIP codes: car wash in 90210
Note these general and location-specific terms—they’ll be the starting point for your keyword research.
b. Google Your Brainstormed Ideas
Now, search for the phrases and seed keywords you’ve jotted down on Google and check what comes up. If you spot any relevant terms that aren’t on your list, add them.
For example, if you’re running a local car wash, your core terms are “car wash”, “car cleaning”, “auto wash”, etc.
Just go to Google and start typing a core term related to your business and take a note what Google suggests.
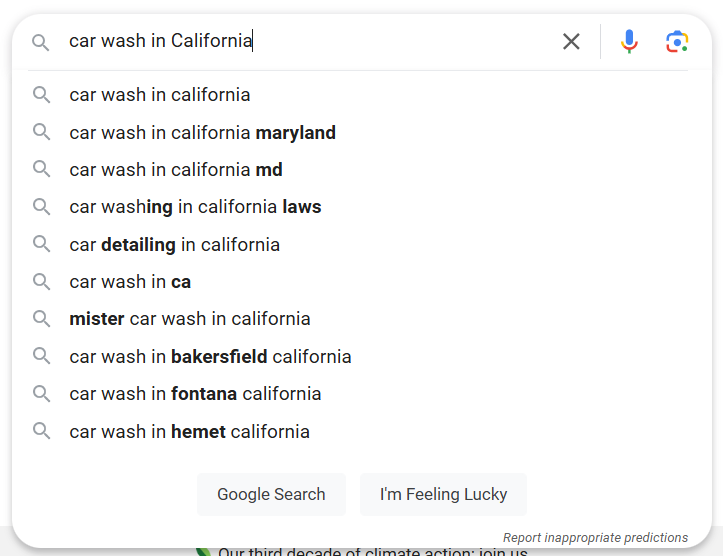
Once you have noted down relevant suggestions from Google search bar, hit Enter.
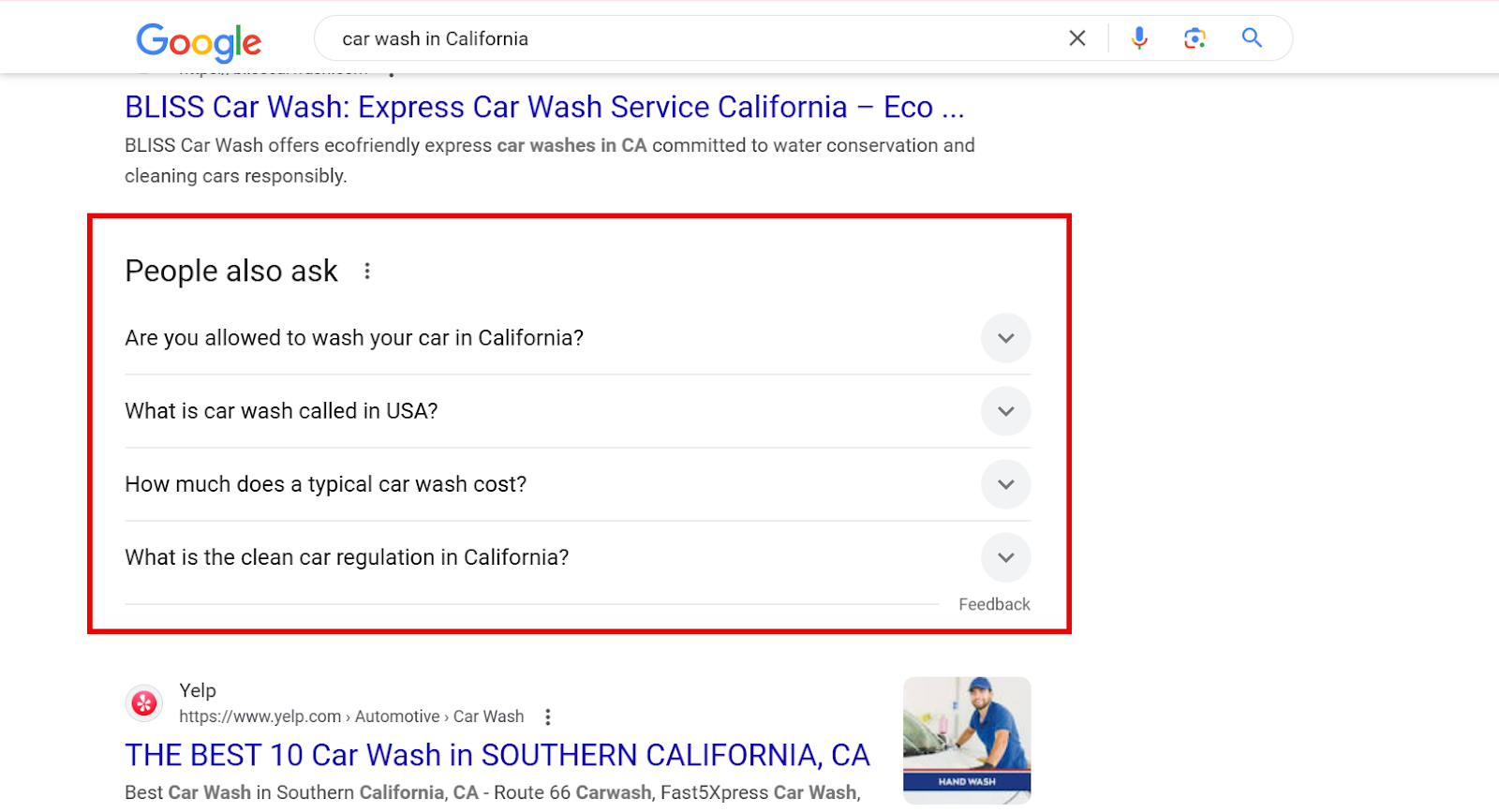
Now, scroll down to the People Also Ask section to see what people are searching for. These are actual questions that your target audience is asking. Take a note of all the relevant questions.
Then, scroll down to the bottom of the SERP to the People also search for section.
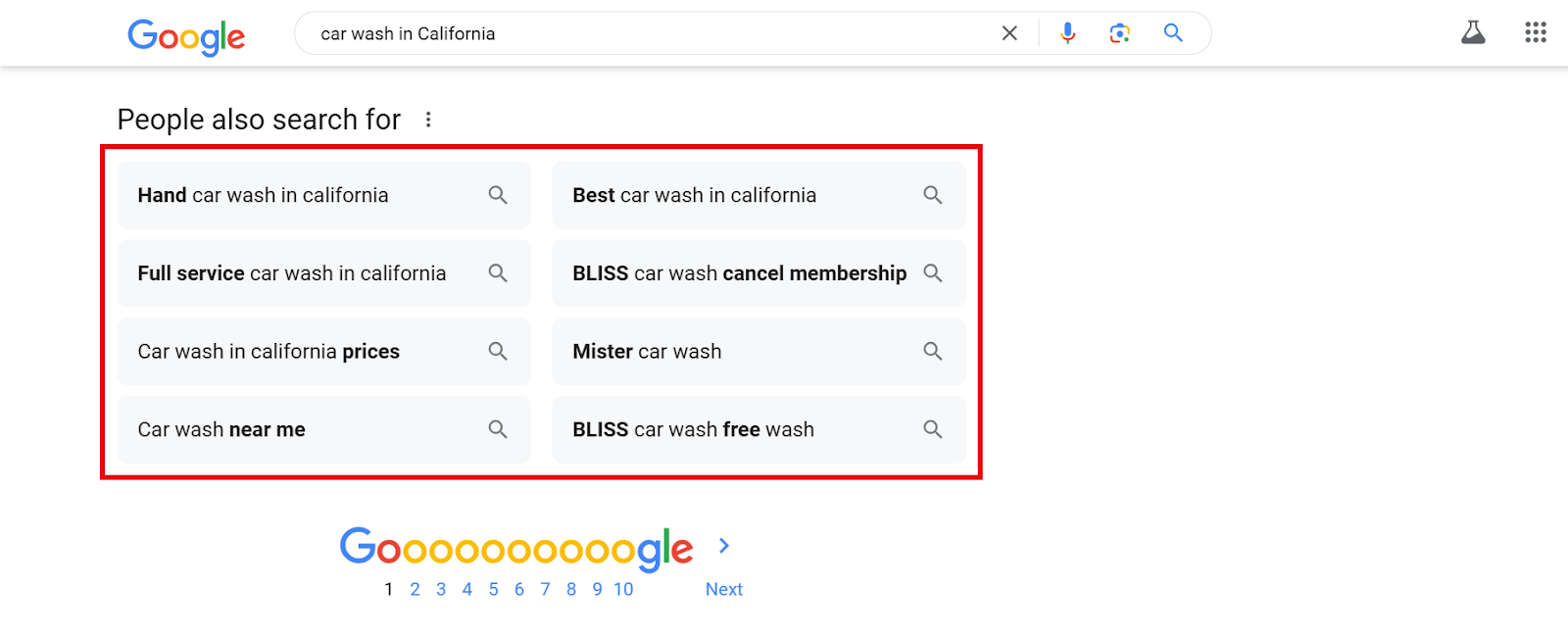
When a searcher makes any query, Google looks into the search pattern of others who have made a similar initial query– then it suggests these related searches based on that pattern.
So, there’s a good chance your target customers are searching for these terms too. Take a note of them as well.
This will give you some basic keywords to start with. But don’t stop here– search all these keywords one by one, and you’ll get some more specific queries.
And if you’re ever stuck, ChatGPT can be a good brainstorming partner. Of course, its suggestions are not backed by any search engine data. It just makes logical and semantic suggestions. So, I use ChatGPT just for inspiration.
Here is a prompt you can use:
Suggest seed keywords for a [business type] in [target region]
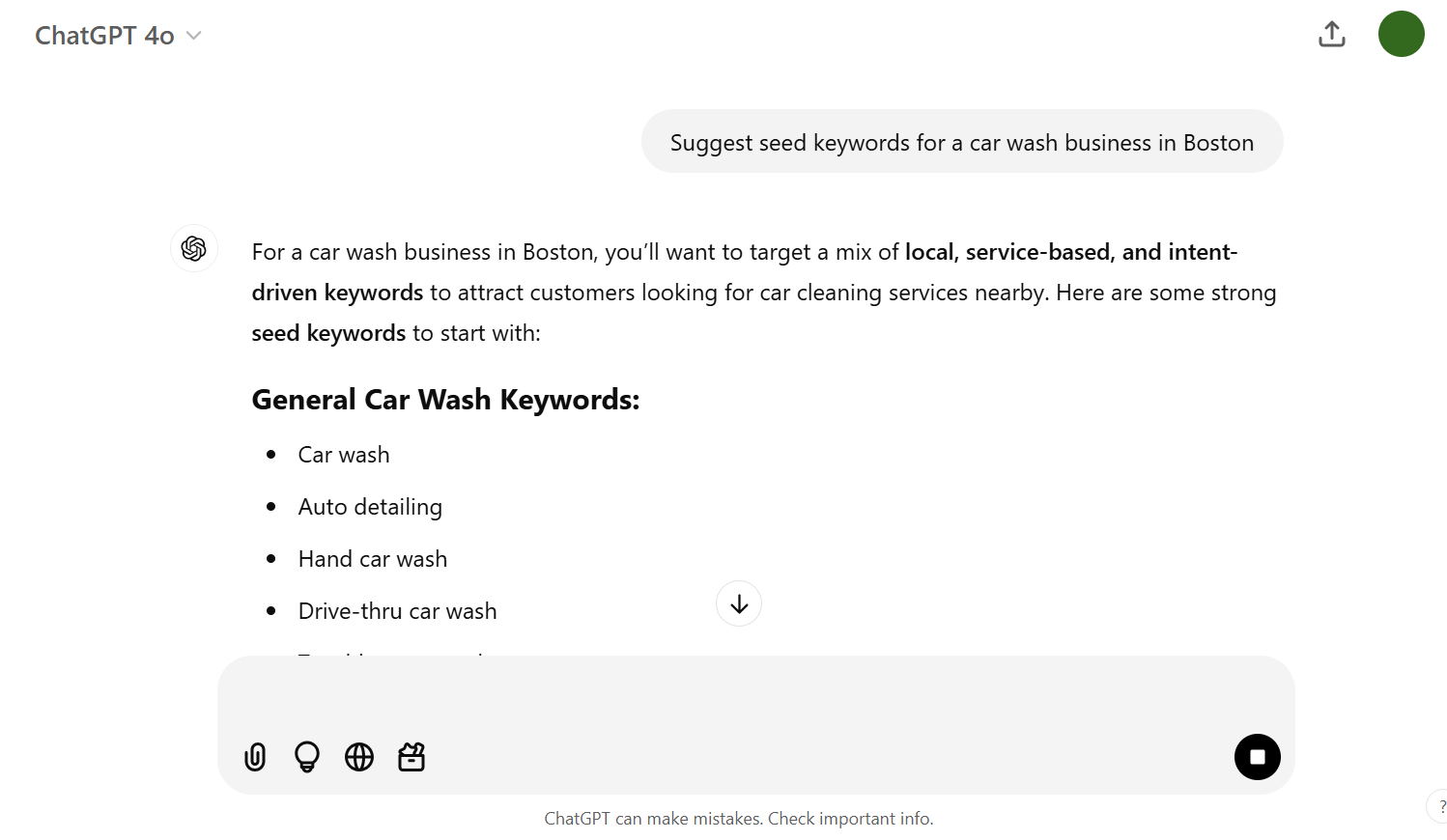
Copy any keywords that resonate with your core offerings and add them to your list.
b. Check Your Competitors’ Website
Before you steal your competitors’ keywords, you need to correctly identify your top competitors.
In the last step, you Googled different terms related to your business. Did you notice which businesses popped up in the organic results the most?
Those are your organic competitors.
Open any of their websites to see what keywords they are targeting.
Here’s an example of what services a local competitor site of a local car wash is offering. When I clicked on each option, I found at least 6-10 more services, like:
→ Headlight Restoration
→ Carpet Shampoo
→ Rim Polish
→ Clay Magic
→ Buff & Wax, etc.
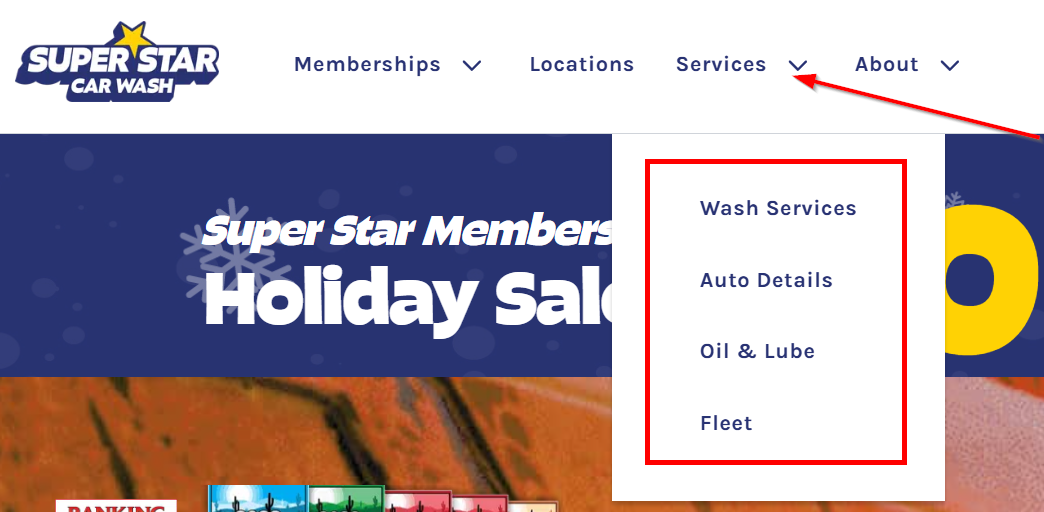
So, if you search your competitor’s website and find products/services that you also offer, add them to your list.
c. Use a Keyword Tool
You can also use online tools, like SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, Google Keyword Planner, etc., for insights about other relevant services.
I, personally, use Semrush, so I’ll explain the steps below using Semrush. Let’s dive right in.
2. Add Local Keyword Modifiers
Now that you have a list of your main services aka seed keywords, you can start using modifiers to extend these core terms.
Modifiers make your core term more specific and easier to rank for.
By adding modifiers, you target less competitive terms and attract customers searching for exactly what you offer.
I use SEMrush’s Keyword Magic Tool for this.
Go to SEMrush Keyword Magic Tool. Type in your first seed keyword and your website’s URL. Then, select your target country and click Search.
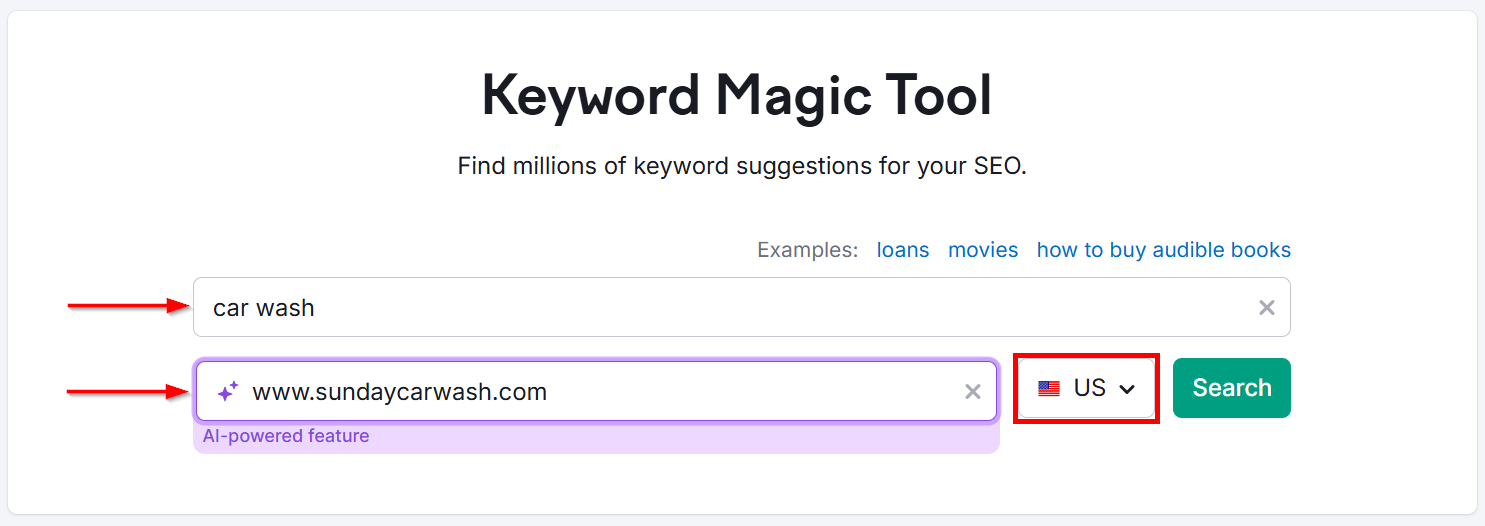
This will give you a list of related keywords, including your seed keyword or a variation of it.
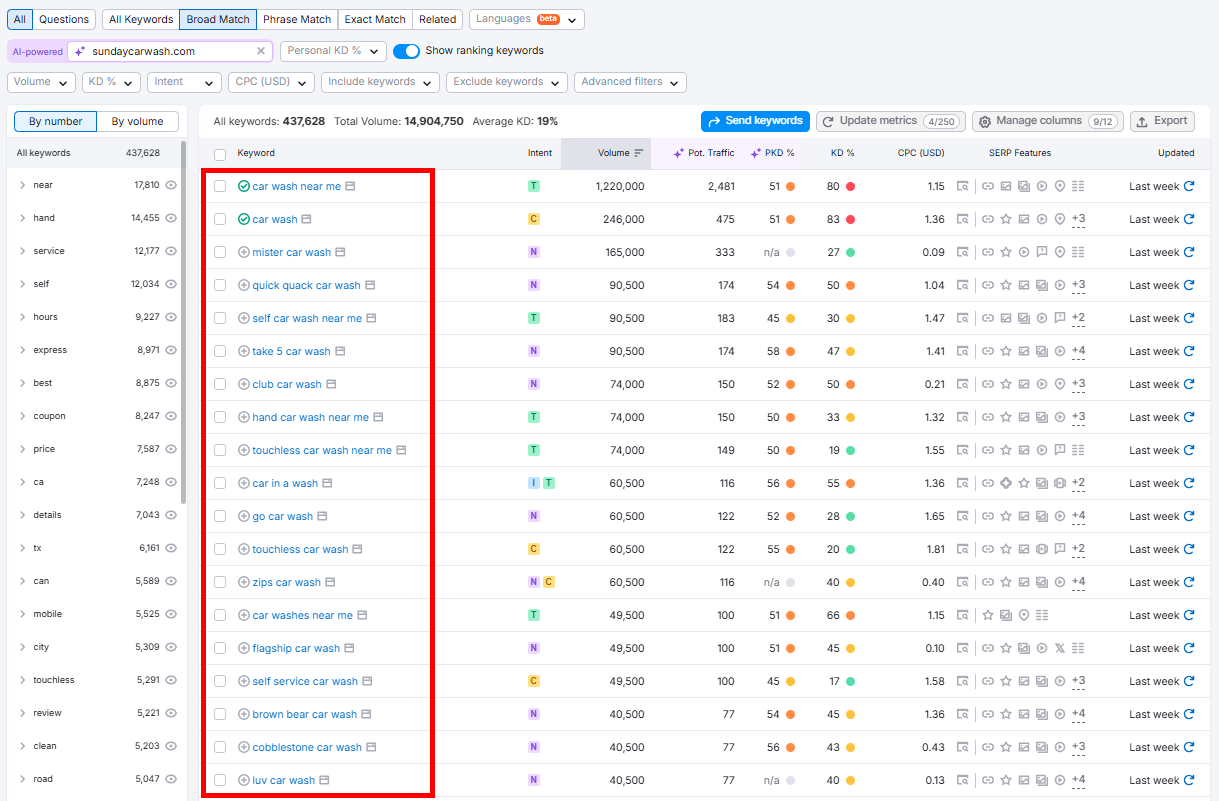
Since I’m doing it to find keywords with local intent, I’ll use different filters to narrow down my research.
First, let’s search for explicitly local keywords, like car wash in california.
Click Include keywords and select Any keywords. Then, type in all your location modifiers and click Apply.
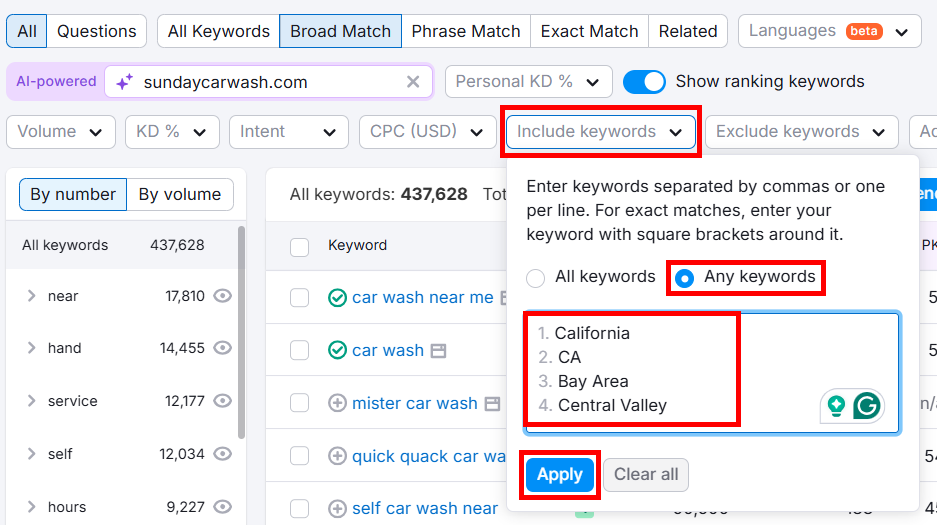
Review the list of keywords and pick the ones that best match your products/services.
If you entered your domain name, check the Personal Keyword Difficulty (PKD %) column. This metric shows how hard it will be for your website to rank for a specific keyword based on your site’s authority and content relevance compared to your competitors.
Click the Personal KD % filter.
Set the range to 0-49 (keywords you have a better chance of ranking for) and click Apply.
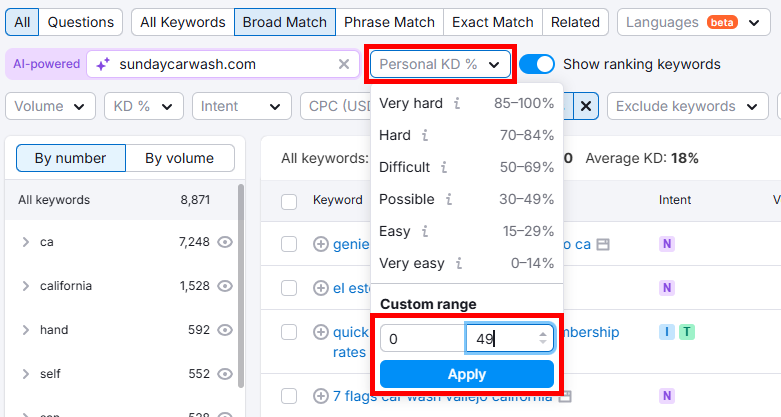
Now the key is picking keywords with a reasonable search volume and PKD.
Select relevant keywords and click the little checkboxes next to them. Then, click the Send keywords button, select Keyword Strategy Builder, and click Apply.
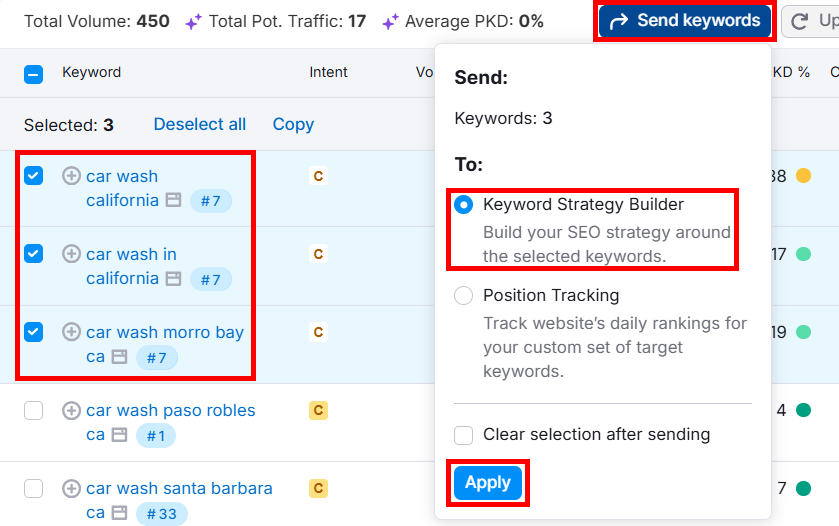
You can use these keywords in the Keyword Strategy Builder to monitor their performance on your site later.
Now, let’s find implicit keywords. These keywords don’t mention your target location explicitly, but terms like self service car wash or car wash near me.
Move your location modifiers (the ones you added in the Include keywords filter) into the Exclude keywords filter to hide location-specific terms.
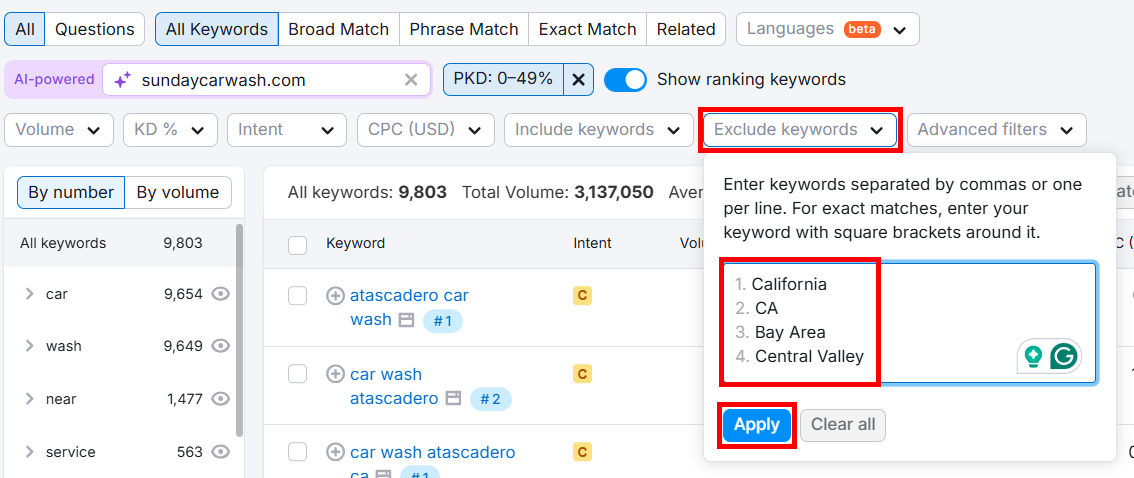
Now, if you want to see only local map pack results, click Advanced filters > SERP Features > Local Pack. Then, click Apply.
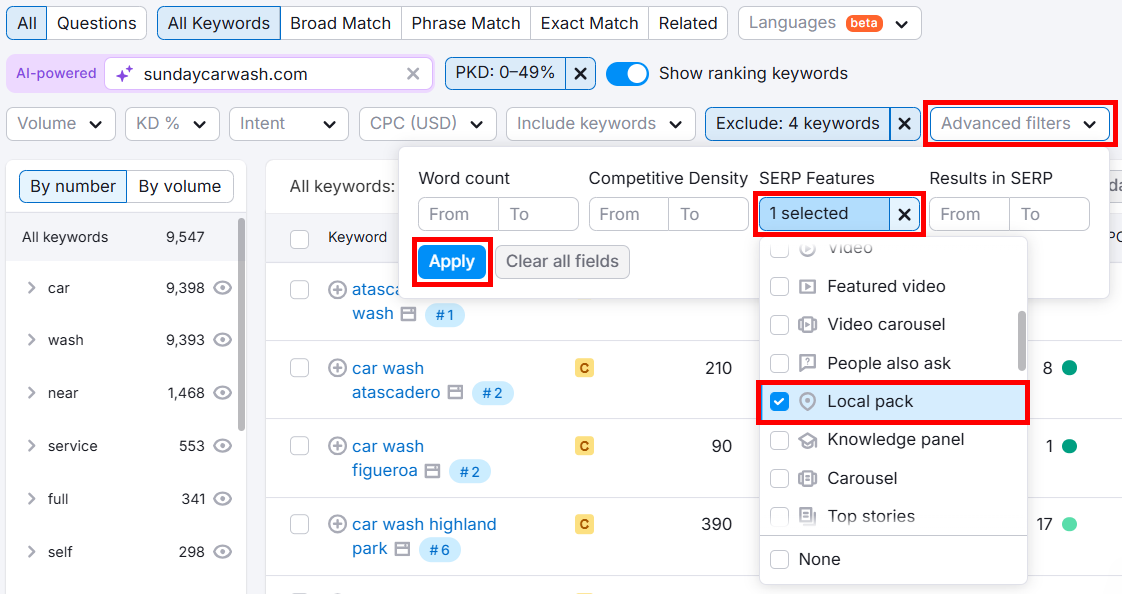
You’ll get a list of super-targeted and highly relevant keywords. Play around with the Volume and KD columns to find any services you might have missed.
3. Analyze Local Metrics
Now that you have a list of saved keywords, you can review the metrics for each one and prioritize terms that are easier to rank for in your target location.
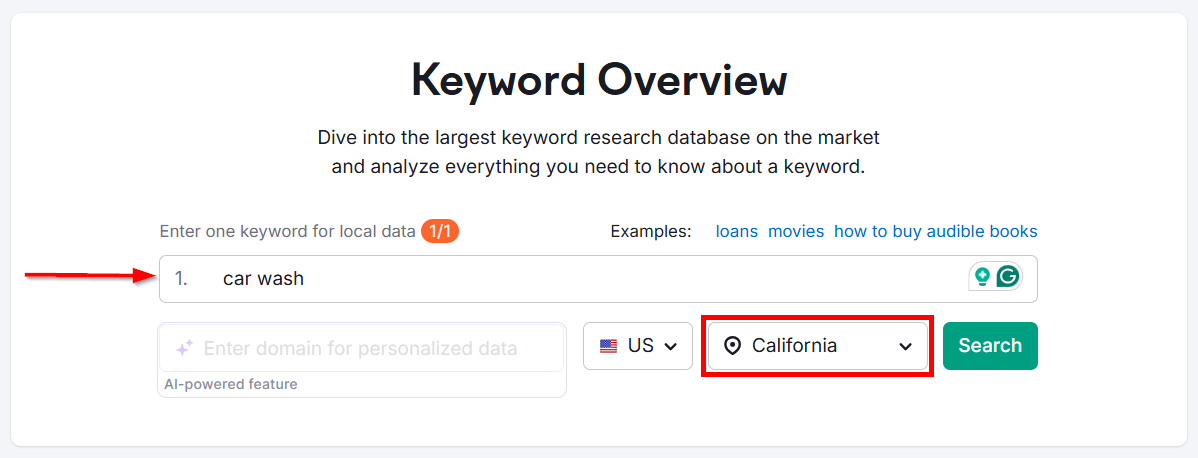
Open the Keyword Overview tool and type one of your seed keywords. Select your location and click Search.
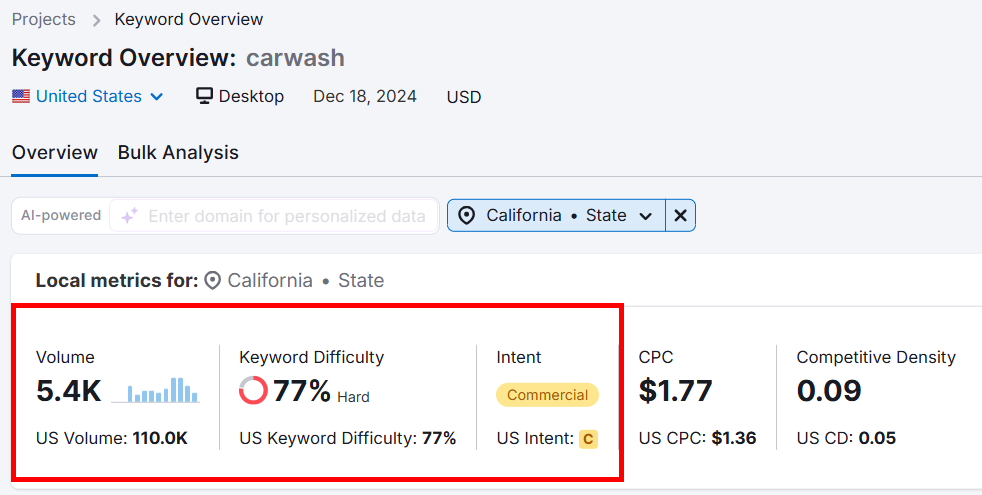
The overview report will show important local data, such as search volume, keyword difficulty, and search intent.
If you’ve been following along, you must have a spreadsheet of your keywords. So, you can use Semrush Keyword Strategy Builder (previously called Keyword Manager) to prioritize the ones with the most potential in terms of local metrics.
Go to the Keyword Strategy Builder option and click create a regular list under the search bar.
Name your keyword list something relevant to your business. I named it Car Wash. Then, click Create list.
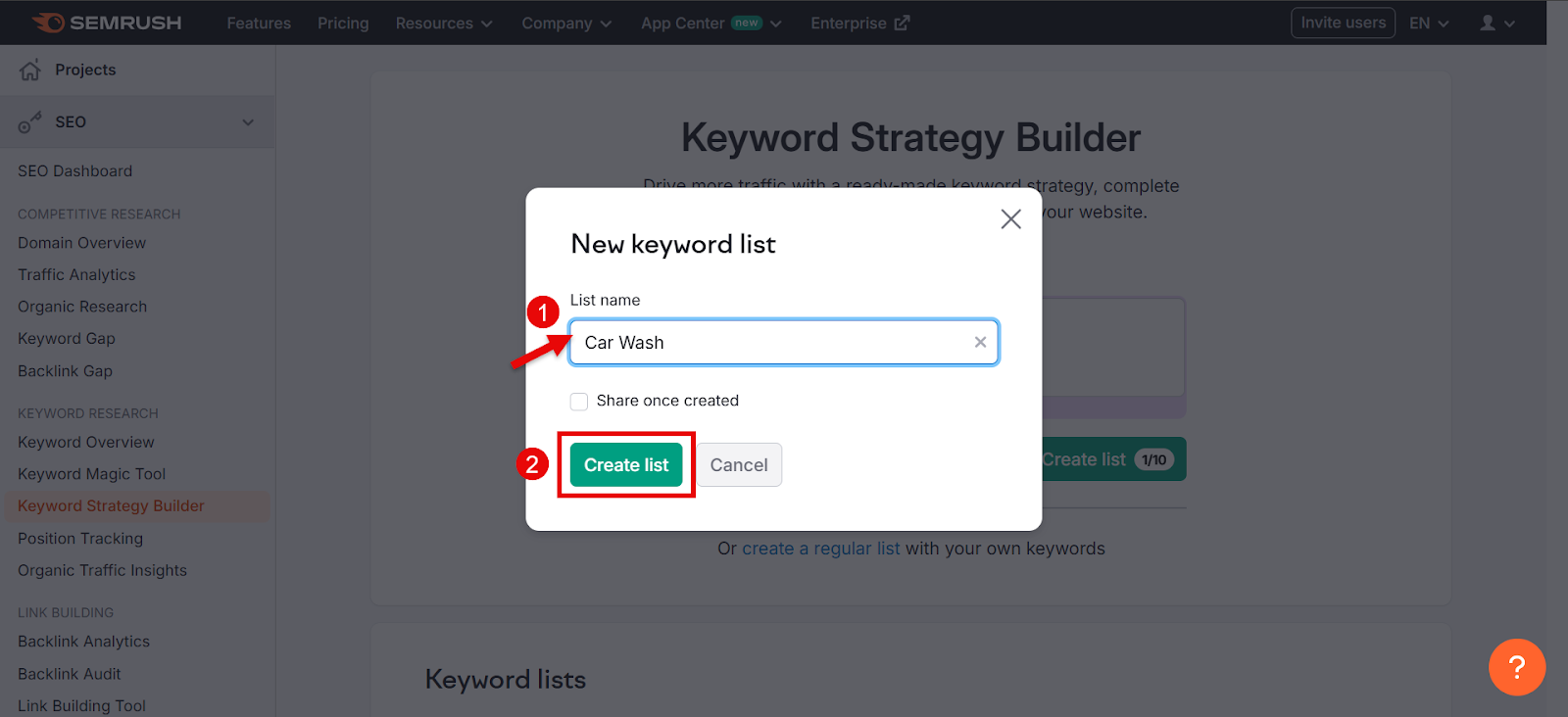
Then, click the Add keywords button in the top-right corner.
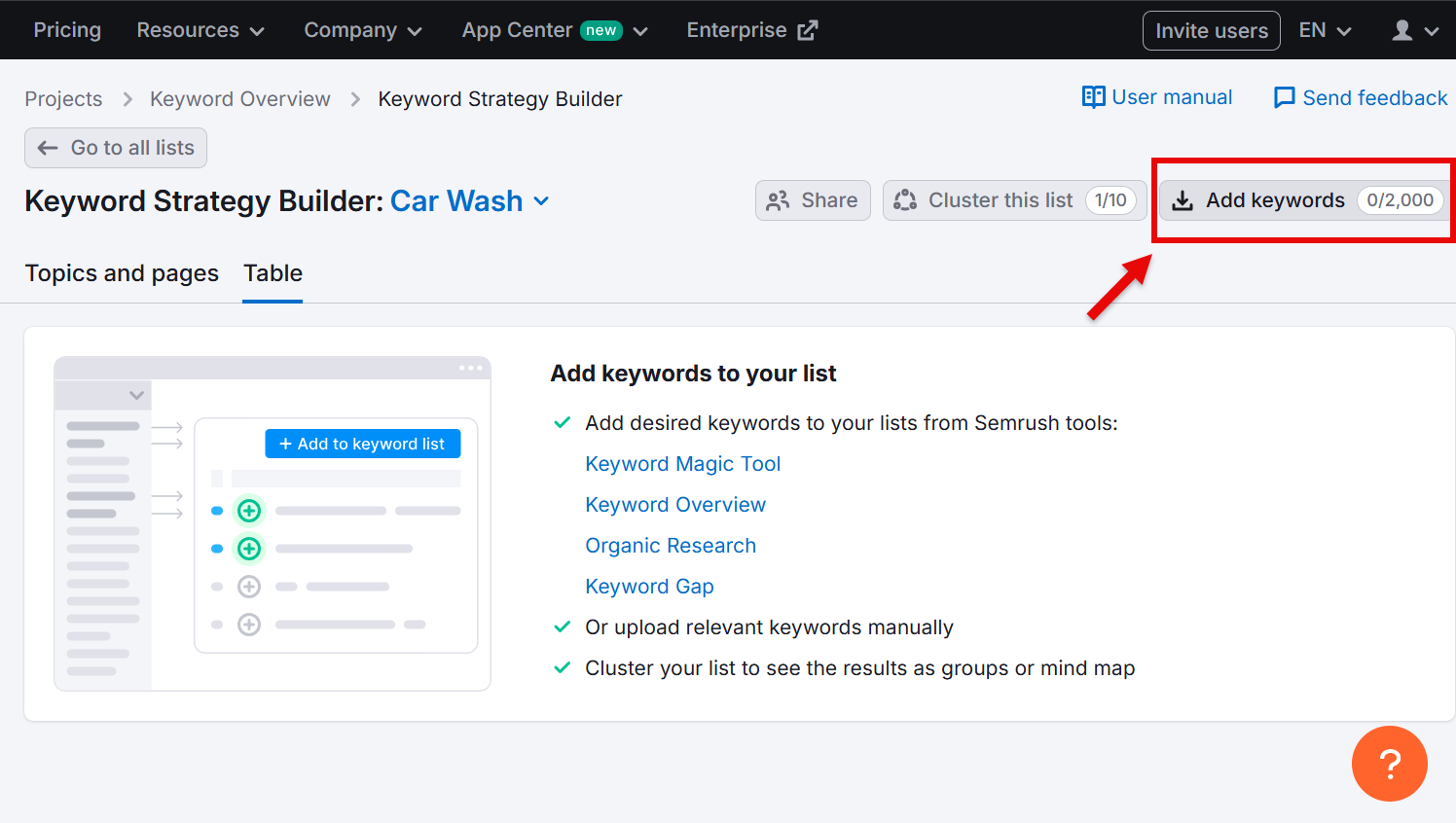
In the new window, add all the keywords from your spreadsheet. Remember, you can add up to 2000 keywords, and make sure you separate each of them with commas.
Once you’ve added all keywords, click Add keywords.
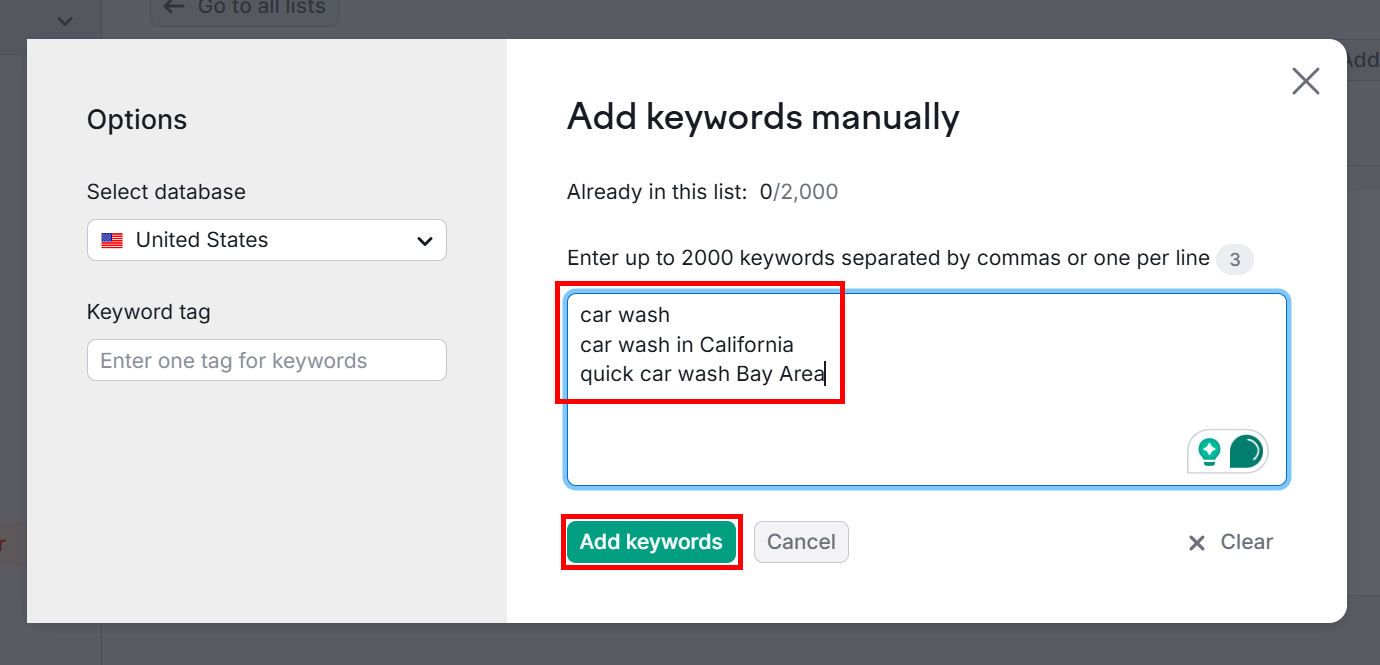
In the Table tab, you’ll see several metrics for all your keywords.
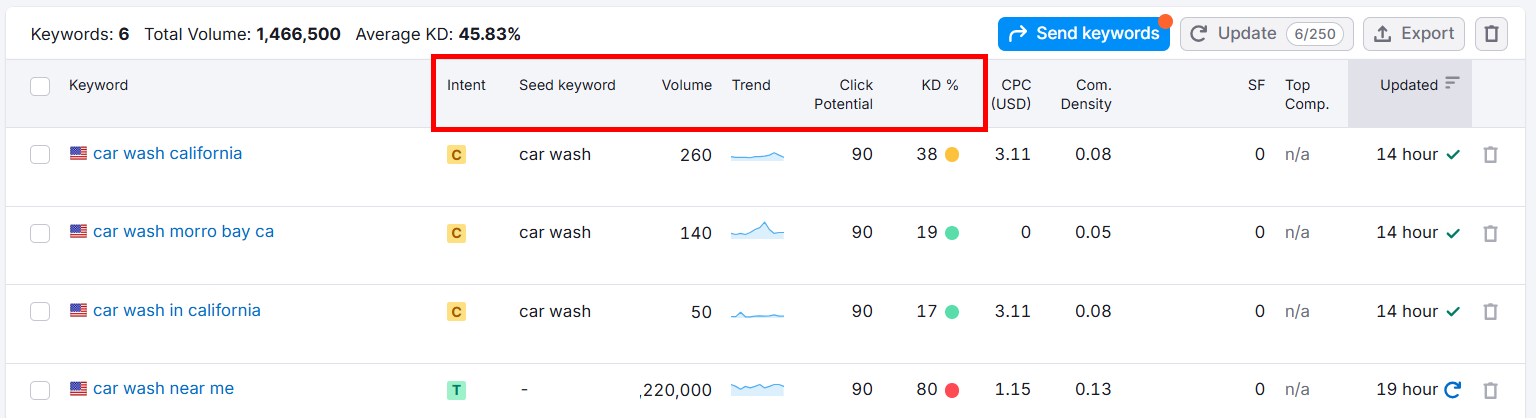
When evaluating keywords, consider these important metrics:
↳ Search Intent: Describes what the searcher wants. Prioritize keywords with transactional or commercial intent to drive action.
↳ Search Volume: Shows how often people search for a keyword each month.
↳ Trend: Tracks how the keyword’s popularity changes over time.
↳ Click Potential: Indicates how likely users are to click on your page for the keyword.
↳ Keyword Difficulty (KD): Measured as a percentage (1% = easiest, 100% = hardest).
Choose keywords with a healthy search volume, low difficulty, and strong click potential. Add transactional or commercial keywords like book car detailing in LA to drive action.
Add these metrics to a spreadsheet and organize them by relevance, search volume, and difficulty.
By using the right keywords in your content, such as full-service car wash Los Angeles or self service car wash near me, your page becomes more visible to the right audience. This increases the chance of attracting clicks and generating more business.
4. Look at Competitors and Keep Improving
Check what keywords your competitors target. You may find gaps or opportunities they’ve overlooked. Keep refining your keyword list over time so you can stay ahead in local search results.
You can also find local keywords by analyzing your competitors’ rankings. To do that, just run a local keyword search on Google.
For example, I searched for “car wash in california” and got these results:
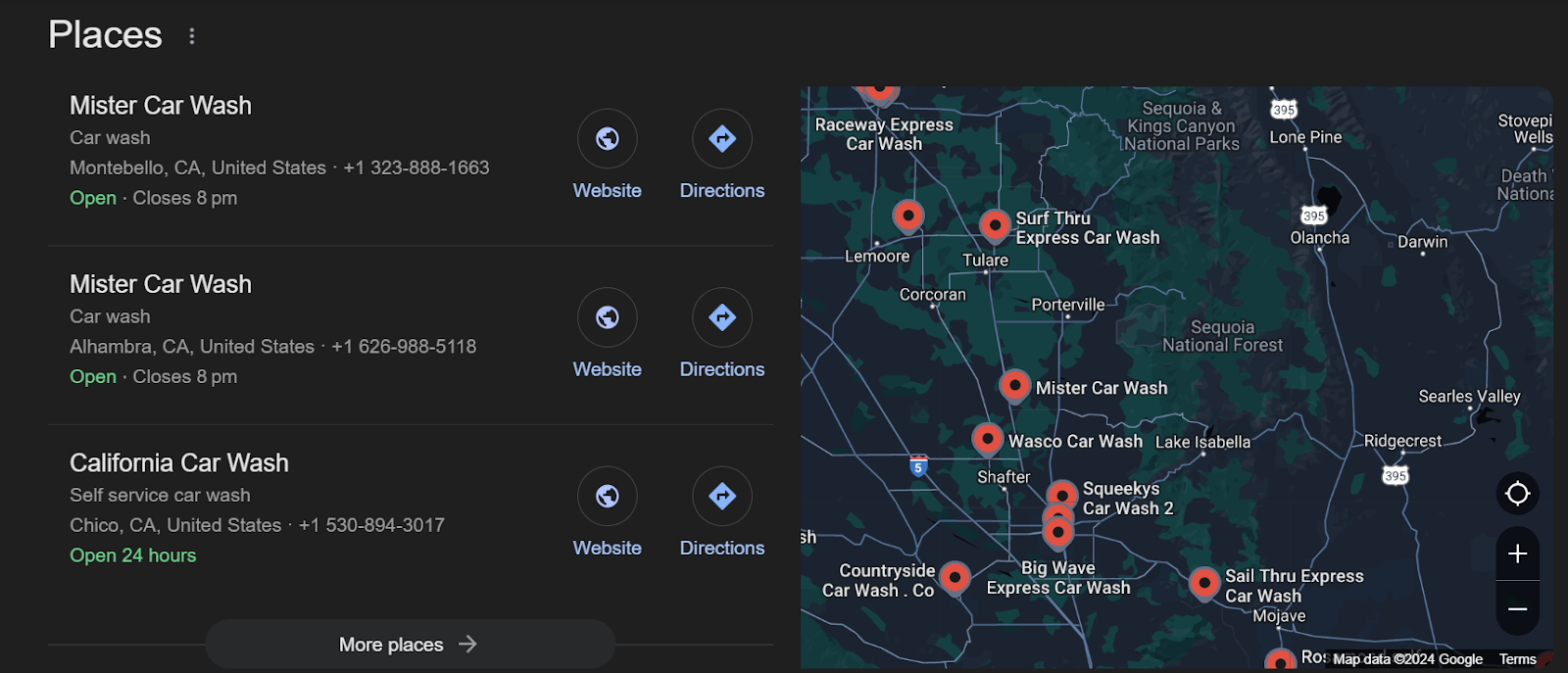
These are the top competitors for my car wash small business.
You can also do a deep dive into your competitors using SEMrush Domain Overview. I’ll show you how.
Go to the Domain Overview option and type your domain. Select your country and click Search.
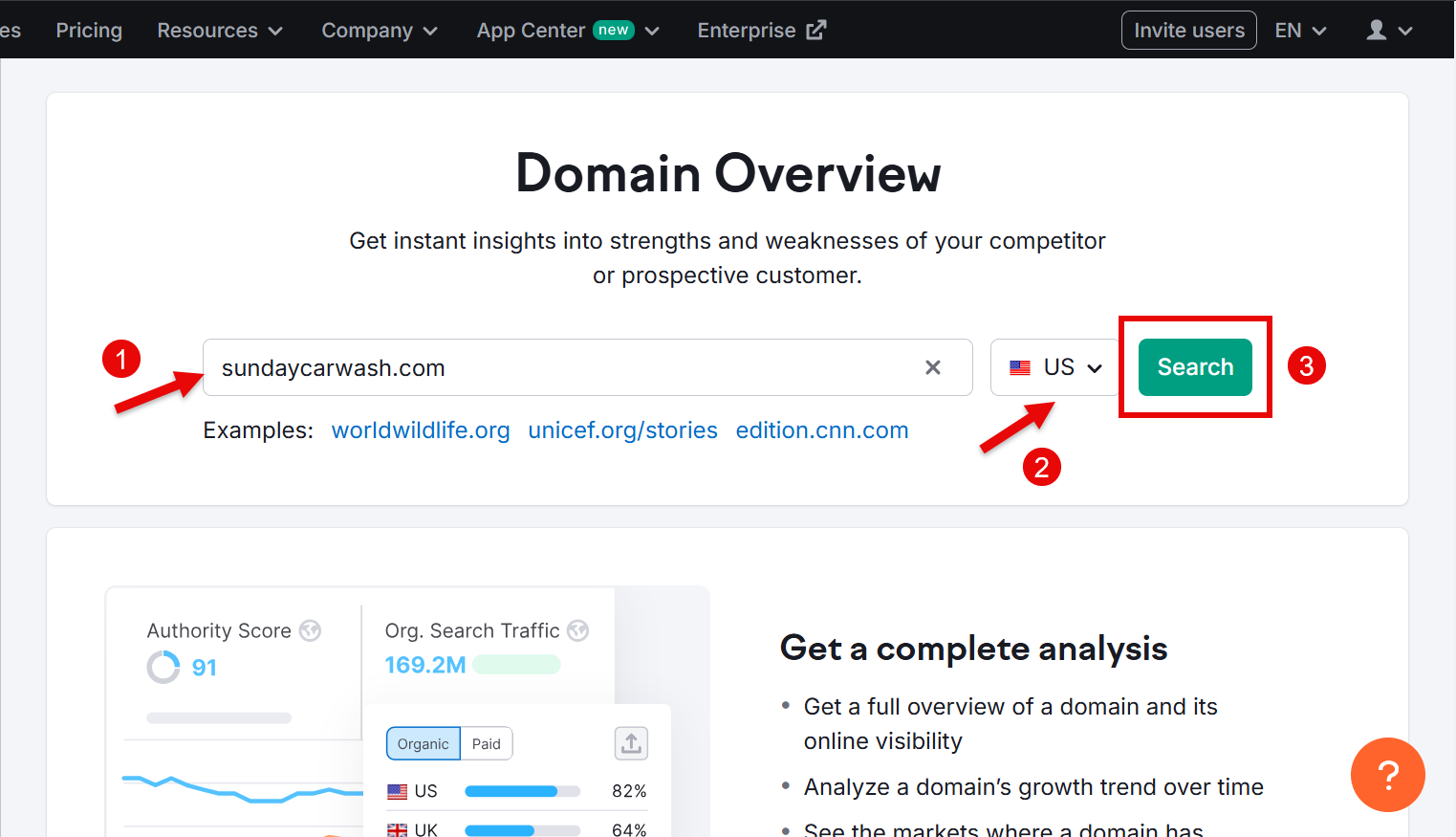
Let the details load and then scroll down to the Main Organic Competitors section. Here, you’ll find all your top competitors. You can learn more about their websites by clicking the View details button.
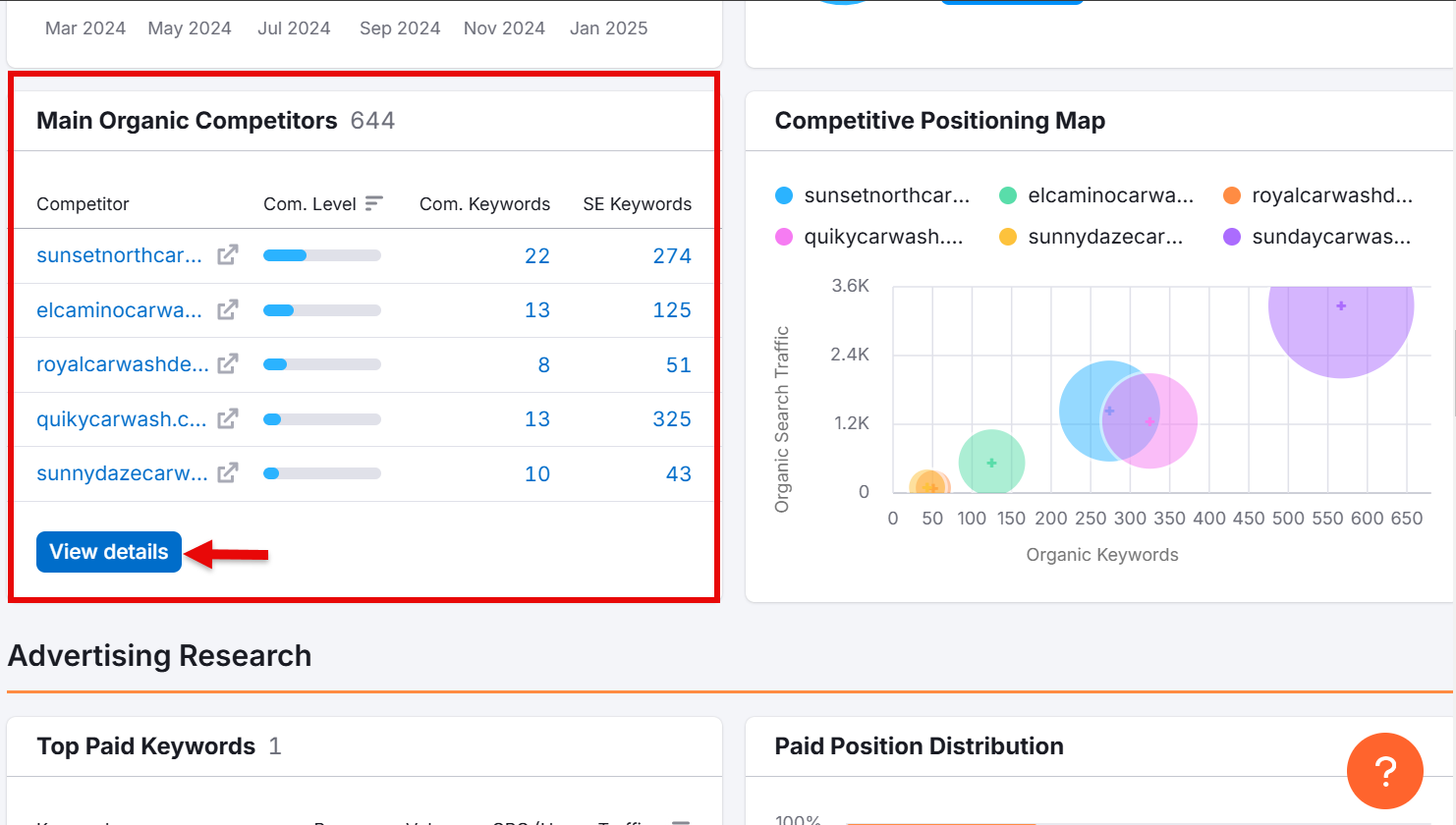
If you have location-specific pages, search the exact URL (e.g., example.com/locations/city).
Switch Root Domain to Exact URL and click Search to find competitors for that specific page.
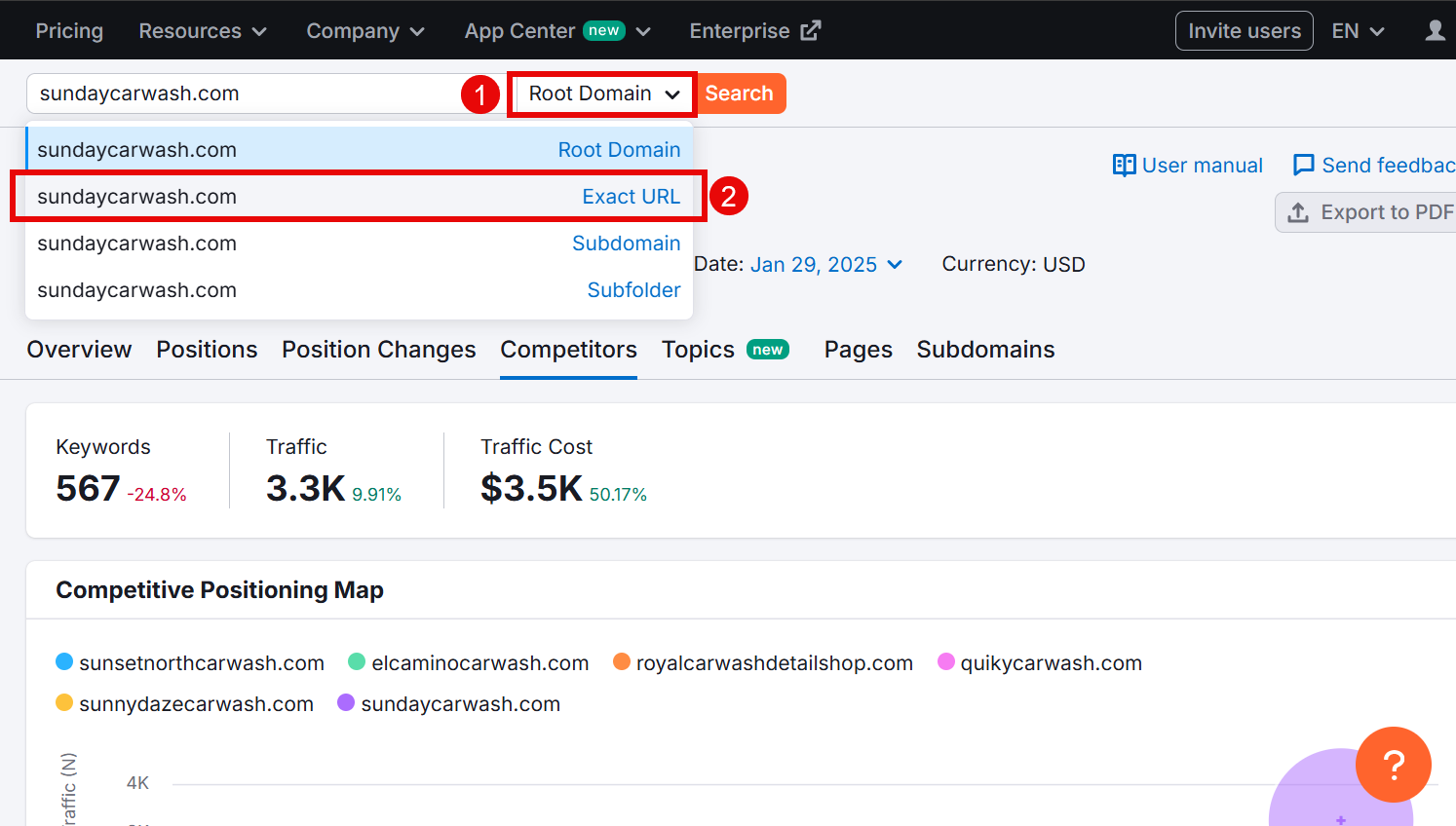
Then, follow the same steps as above.
Once you identify your top competitors, use the Keyword Gap tool to find keywords they’re ranking for that you’re not.
Enter your domain and up to 4 competitors’ domains. Select your target country and click Compare.
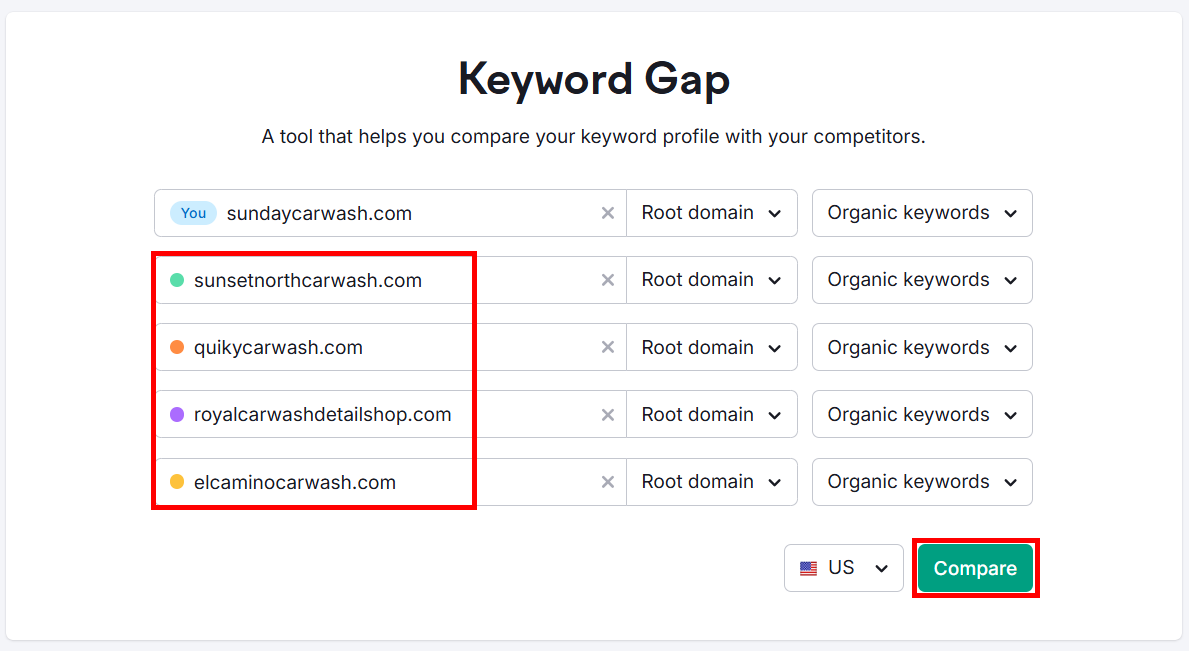
On the next page, make sure you switch to Mobile results in the Device option because most local queries happen on mobile devices.
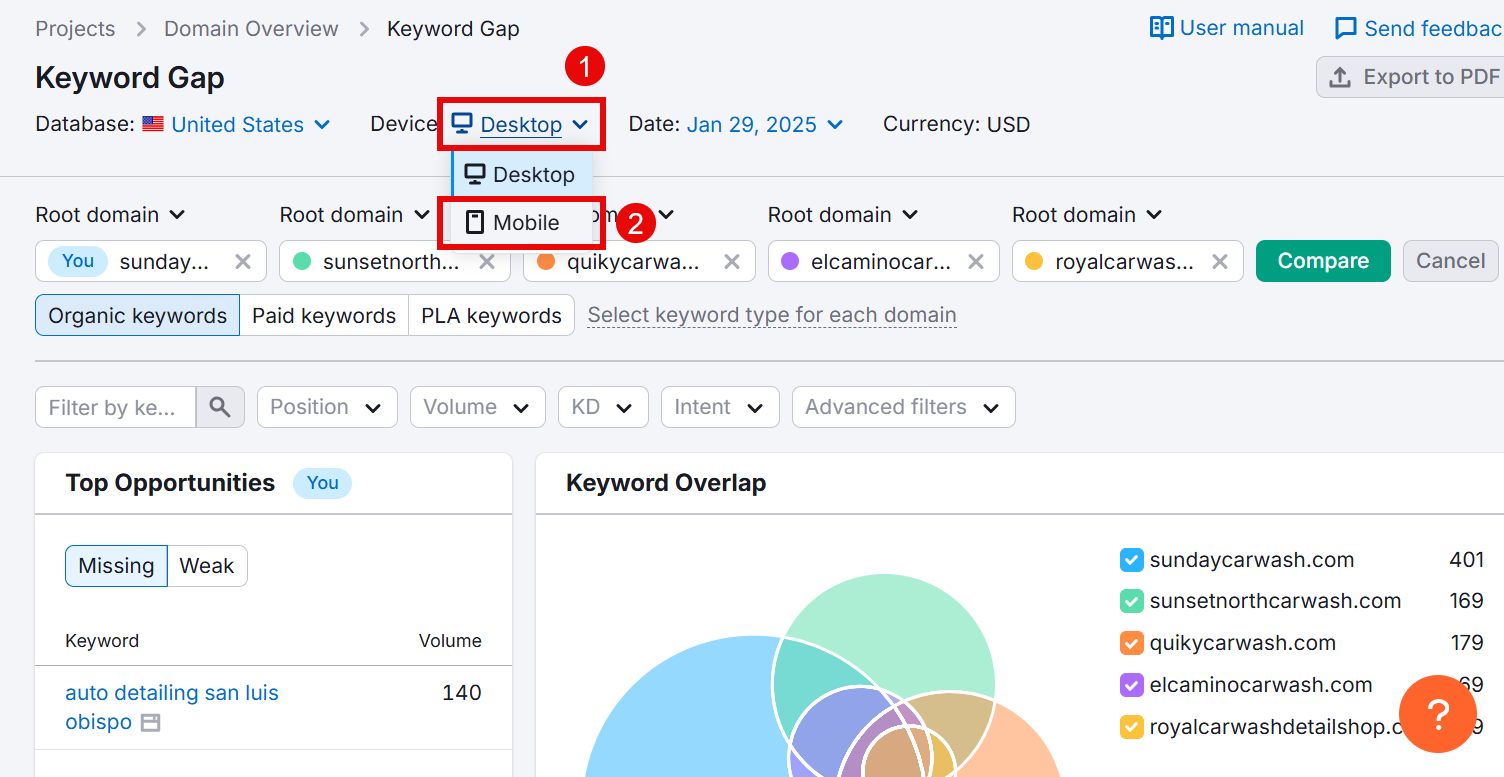
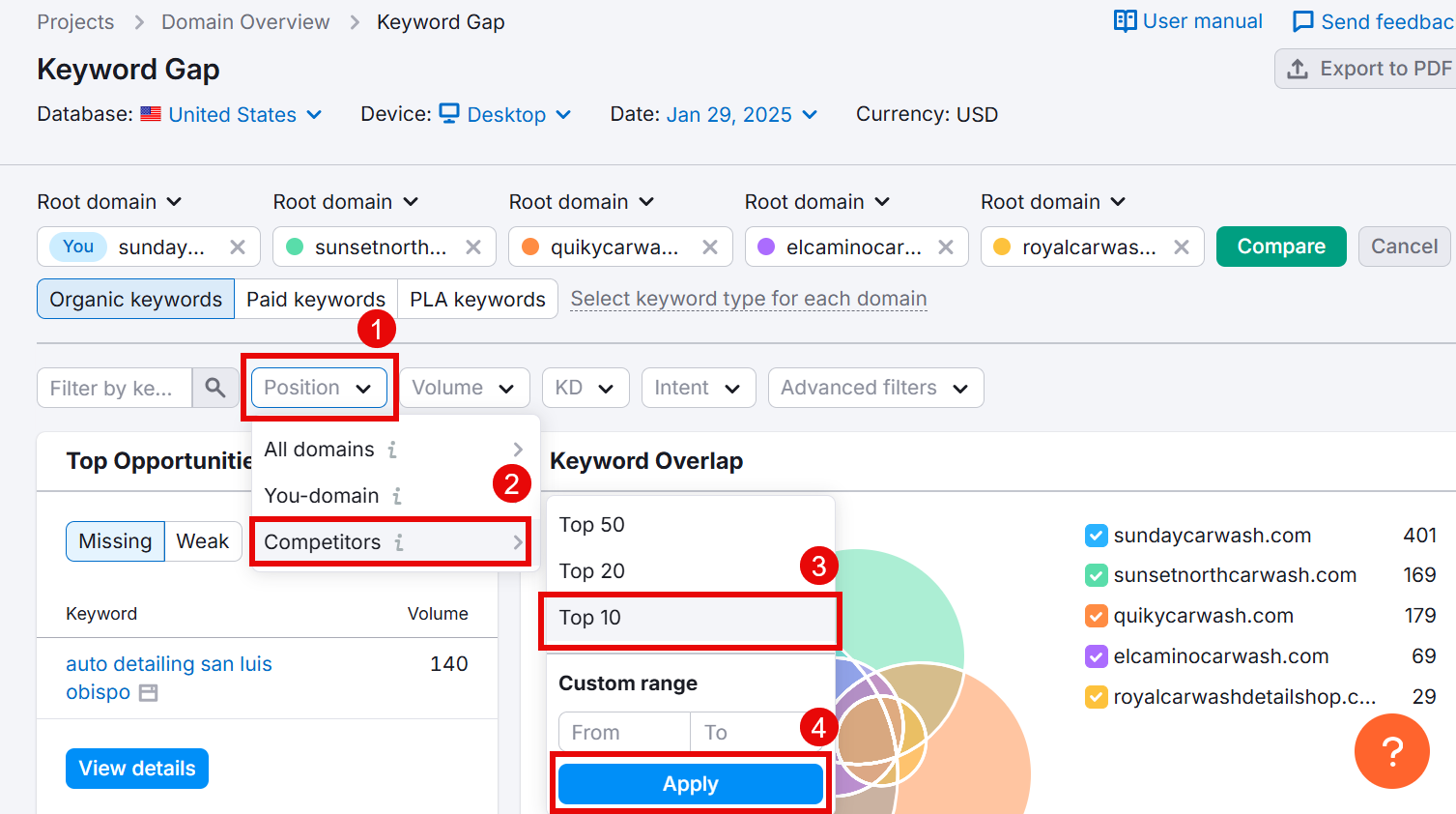
Next, find the terms your competitors are ranking high for. To do this, select Position > Competitors > Top 10 and click Apply.
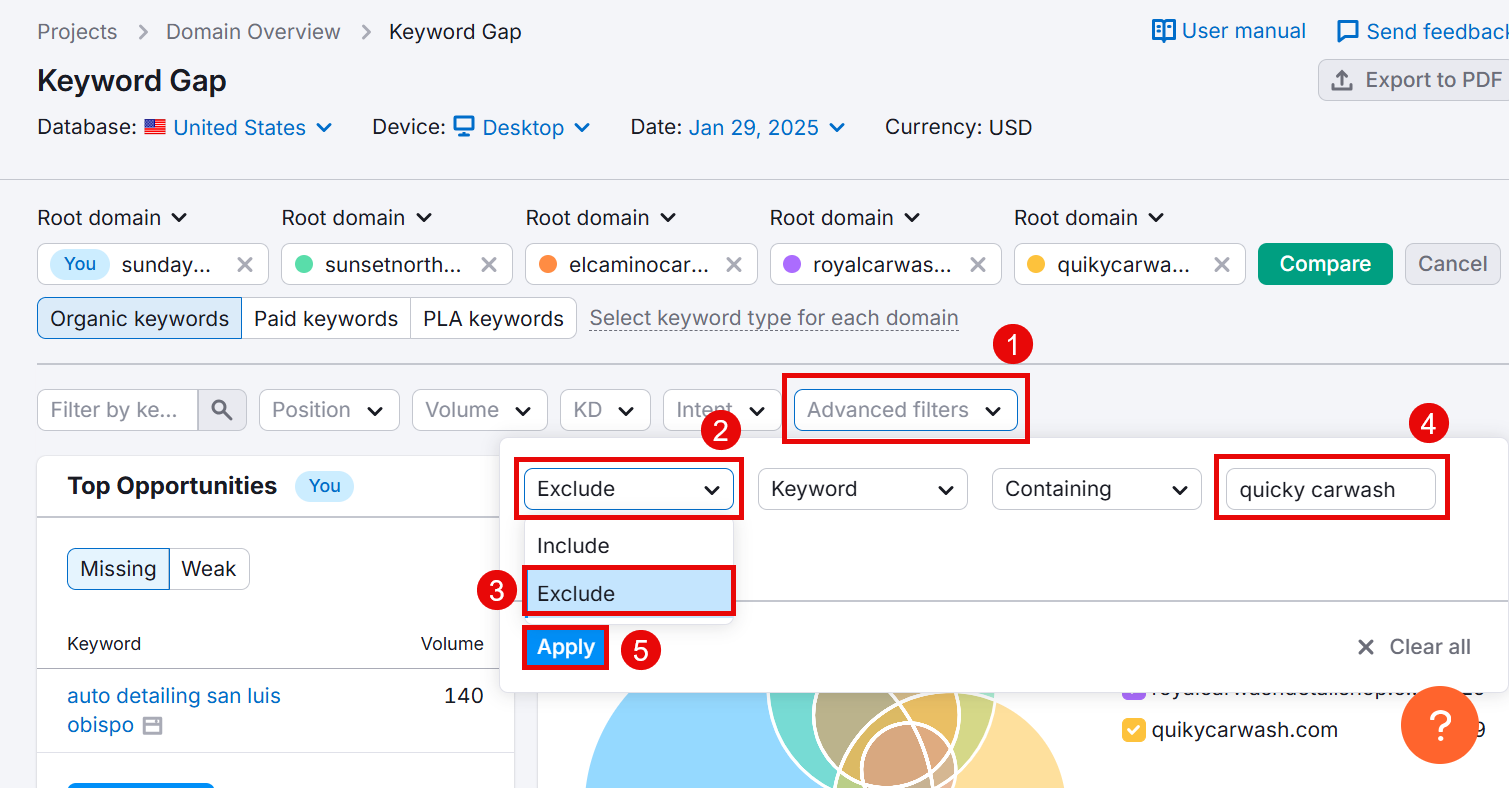
Avoid targeting competitors’ brand names.
To exclude them, go to Advanced filters > Exclude > Keyword > Containing > enter the competitor’s name in the last field > click Apply.
Next, filter for keywords with explicit local intent using your location terms.
Go to Advanced filters > Include > Keyword > Containing > enter your location keyword (e.g., California) and click Apply.
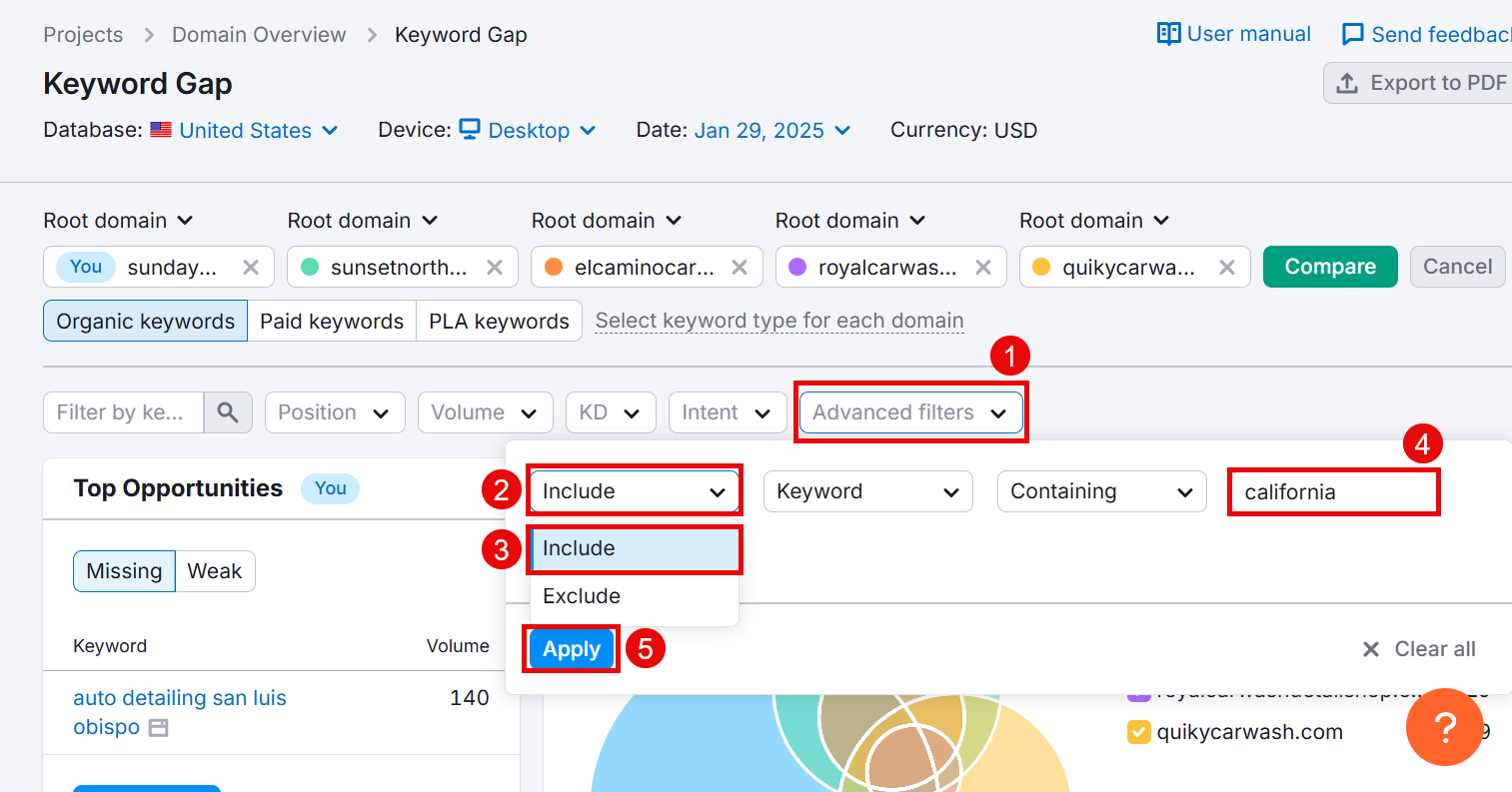
Now, scroll down and check the Untapped tab to see a list of keywords your competitors are ranking for and you’re not.
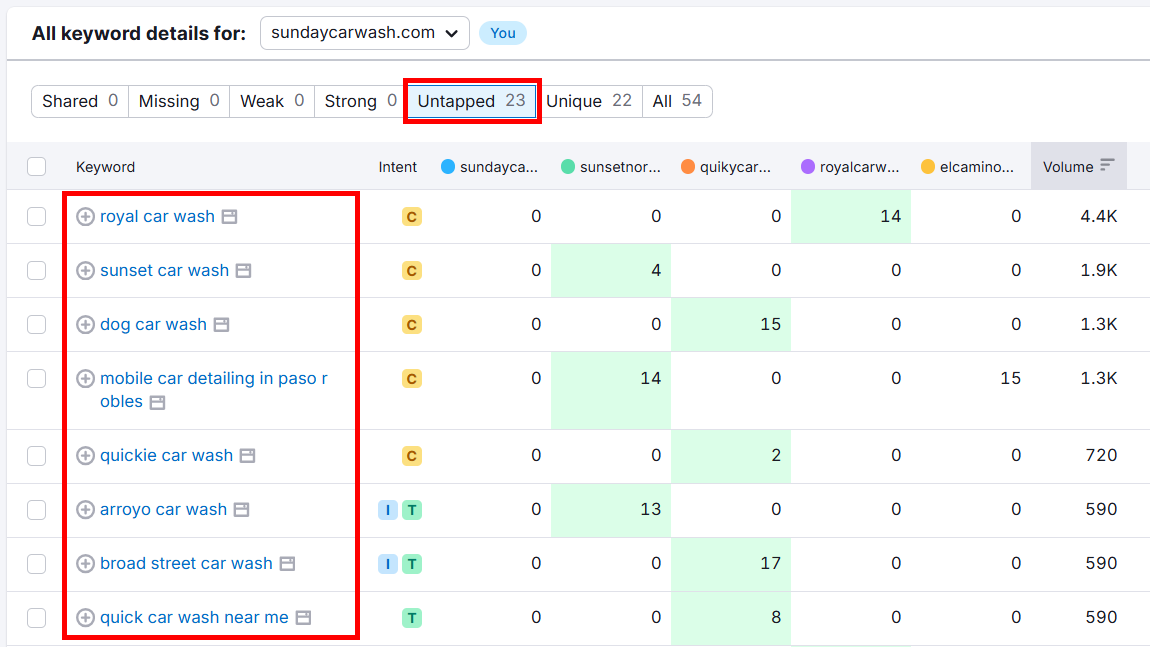
Look through the table and add any relevant keywords to your list.
5. Organize and Map Your Keywords
Now, what to do with your researched keywords?
Start by figuring out which pages on your website will target specific keywords.
This tells search engines which page is most relevant for a query, prevents your pages from competing with each other, and helps organize your site for better rankings.
I use SEMrush Keyword Strategy Builder to do this. It automatically groups your keywords by relevancy and search intent, making content planning simple.
Assuming you have your keywords list, open the Keyword Strategy Builder option. Scroll down to the Keyword lists section and open your list.
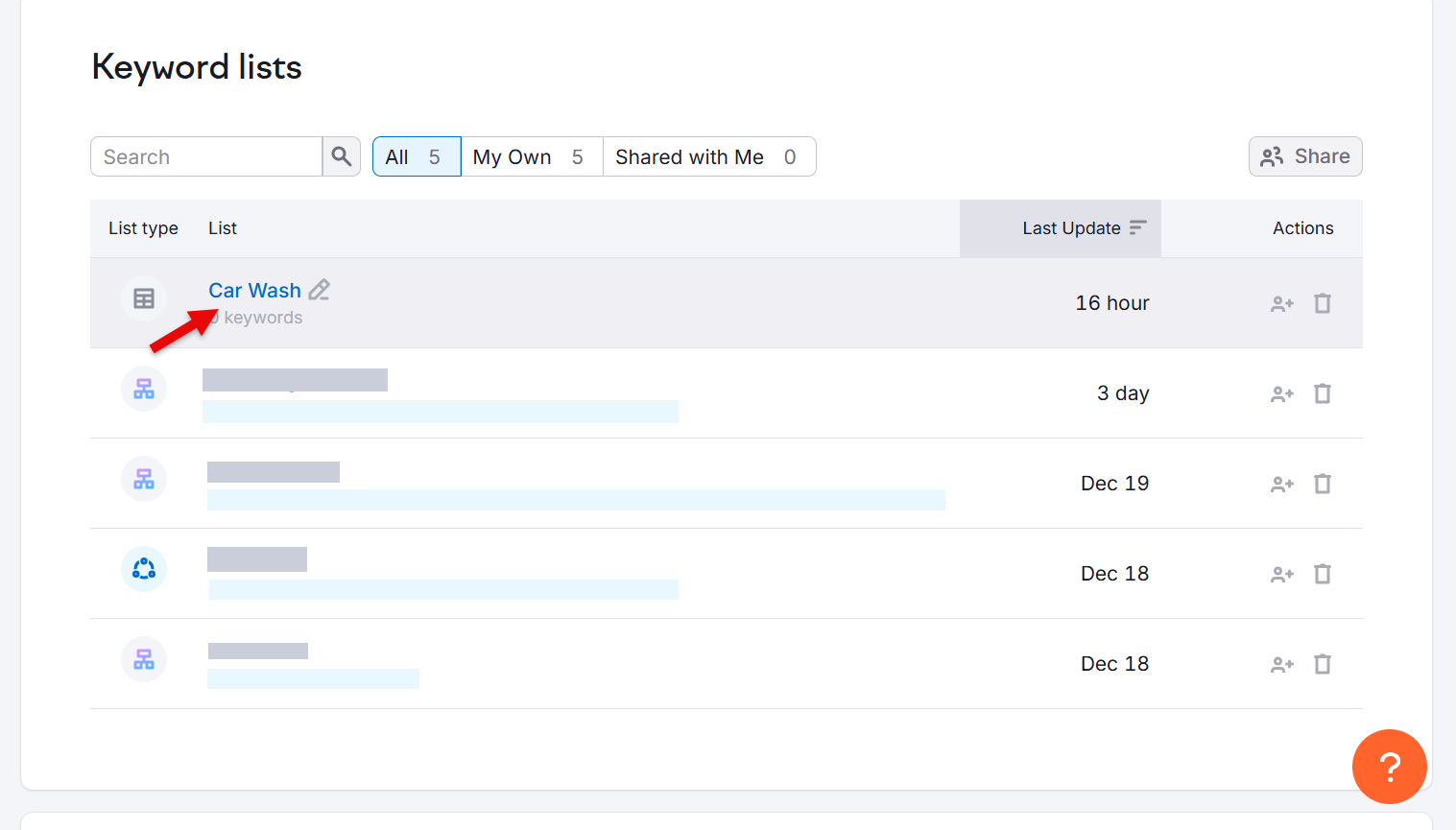
If your keywords are in a spreadsheet, click create a regular list.

Next, click Add keywords and paste your terms into the provided space.
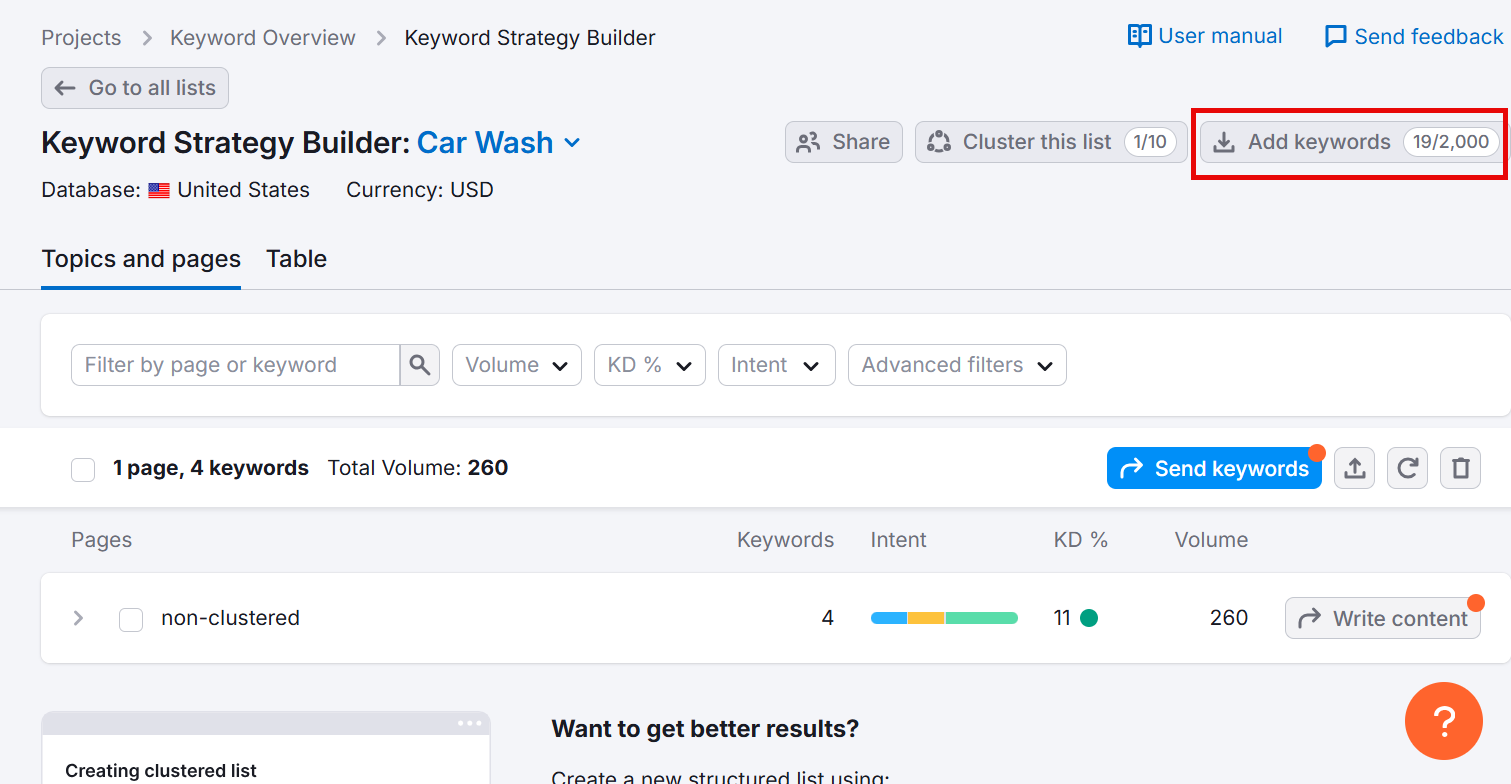
Now, open your list, go to the Topics and pages tab, and click the Create list button.
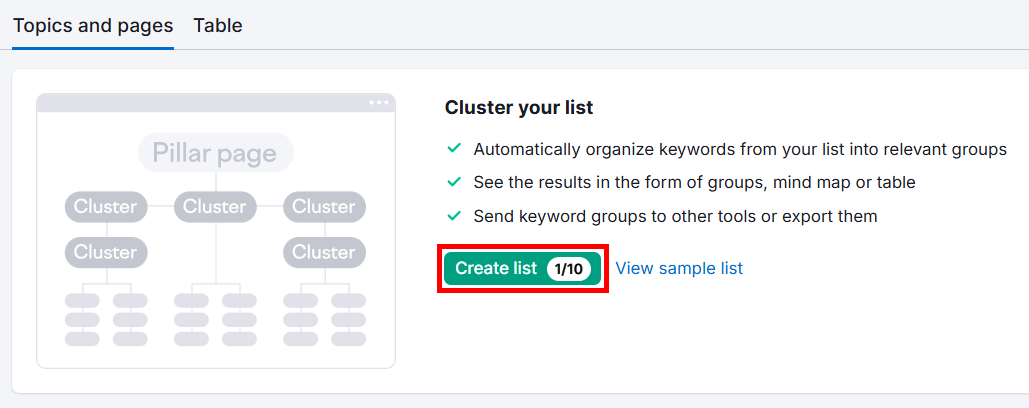
This might take a few minutes, depending on how long your keyword list is. Once its done, you’ll see all your keywords grouped into pages where each page focuses on a primary keyword.
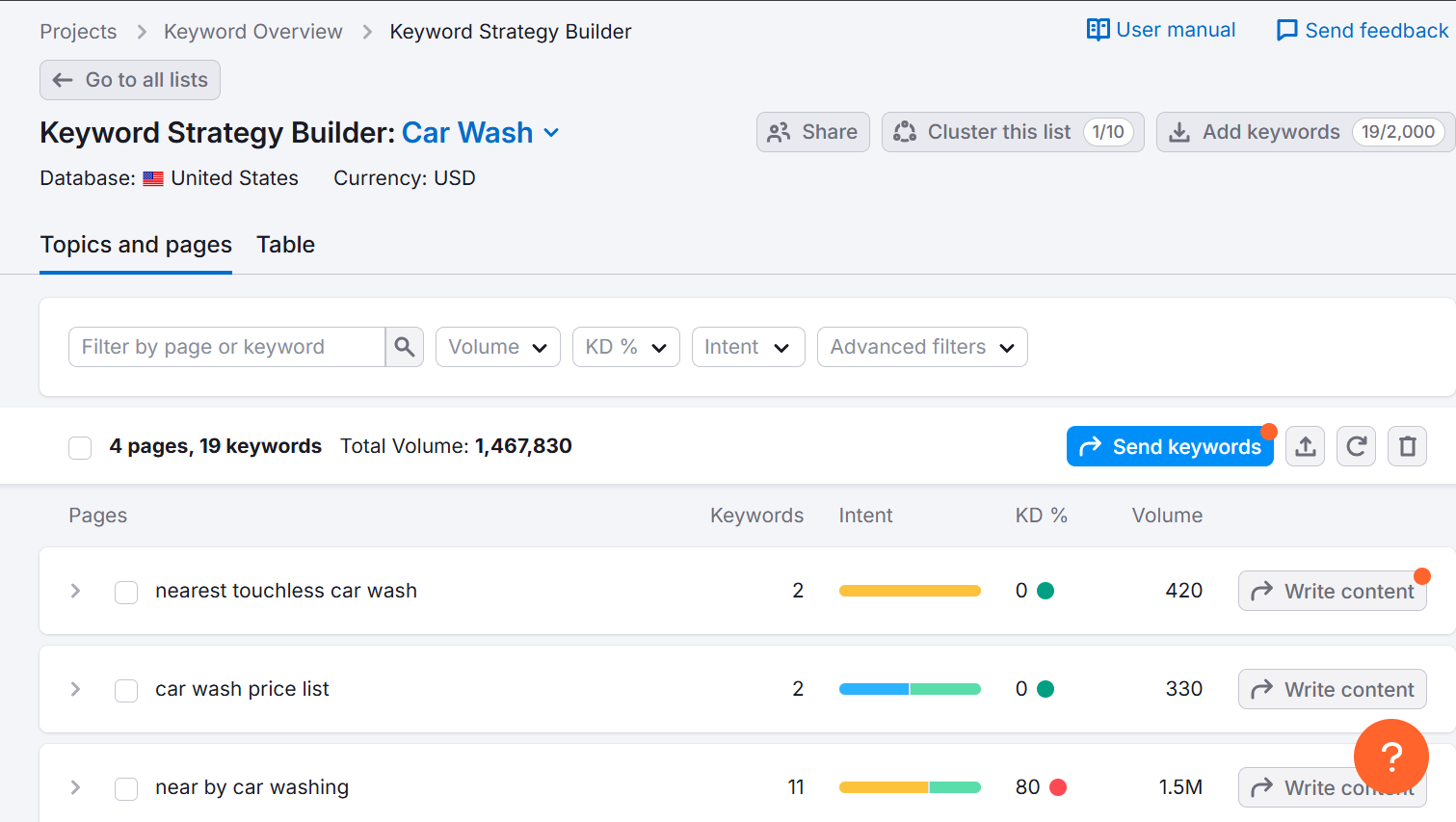
If you are keen to learn more about each page, click the small arrow next to it. It will show you the secondary keywords to target for that page. You’ll also see some content references for the page from top-ranking pages.
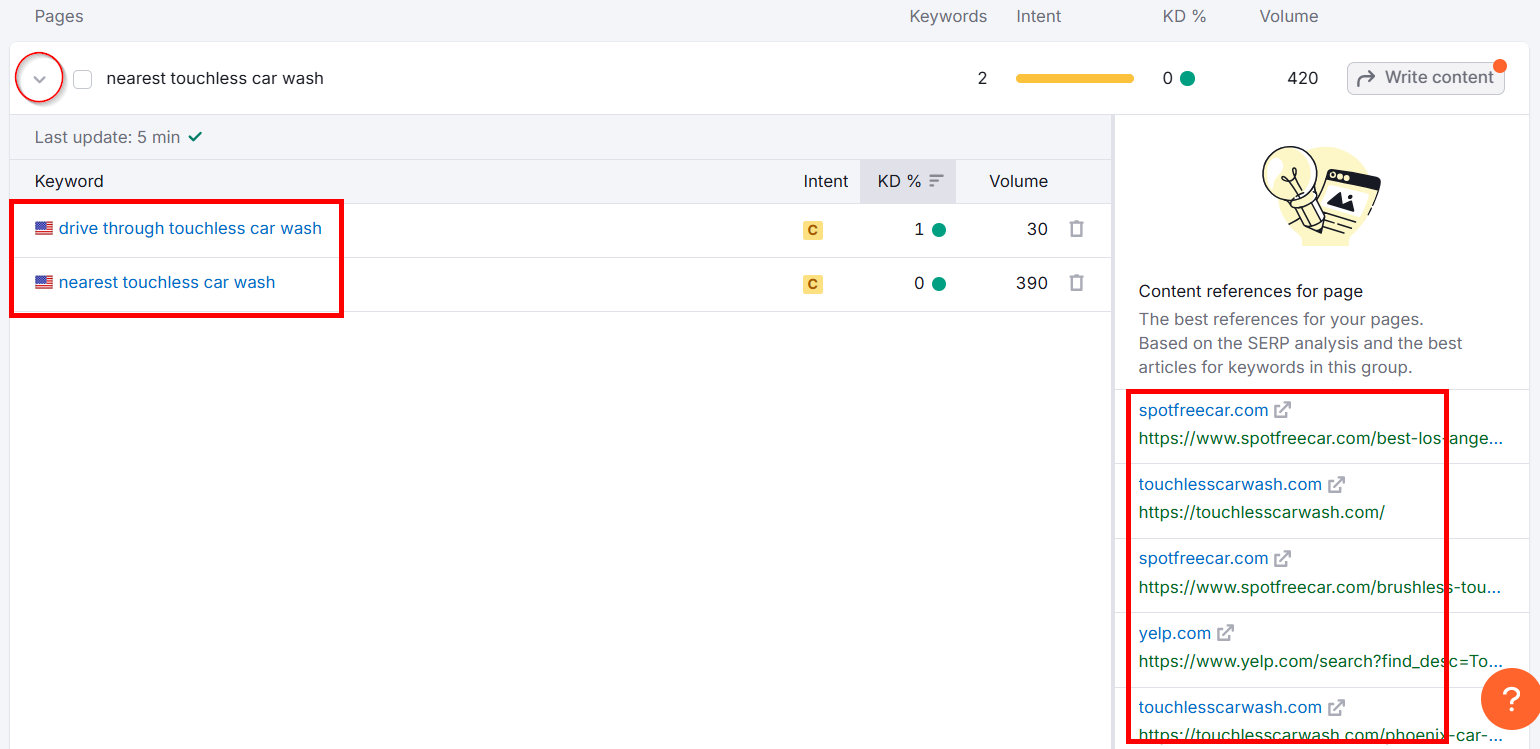
Check the top-ranking results to see what pages and content you need.
How to decide if a keyword needs its own page?
Just because you have a set of similar terms doesn’t mean each one needs its own page.
Check the current search results for top-ranking pages related to each keyword.
If a top-ranking local competitor has a dedicated page for Car Seat Cleaning, that’s a strong indicator you might need one too.
If broader pages are ranking well for related terms like Car Interior Cleaning it might mean you can cover multiple variants on one comprehensive page.
So, let the SERPs guide your strategy: look at what’s ranking, and consider whether your audience would find it helpful to have a separate, dedicated page for that keyword.
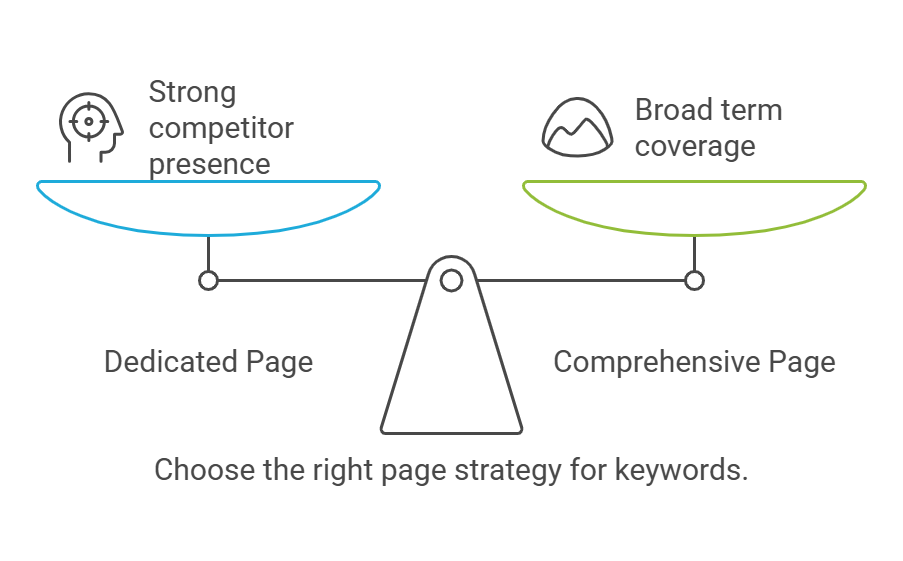
Once you’ve identified which keywords should stand alone and which can be grouped, map them to either existing pages or plan new pages that address these terms directly.
↳ For existing pages: Assign the URL and optimize the content with your target keyword. Use tools like SEMrush’s On Page SEO Checker for helpful recommendations to match top-performing content in your area.
↳ For new pages: Set a target URL and plan the content to match search intent. Include answers to user questions, detailed information, and the right media (videos, images, FAQs) to meet local needs.
And don’t forget to keep track of all URLs and their assigned keywords in a simple spreadsheet. A basic spreadsheet can serve as a keyword-to-URL map. Include columns for:
→ Target Keyword
→ Assigned URL
→ Action (e.g., “Optimize Existing Page” or “Create New Page”)
→ Status/Notes
Keyword mapping isn’t an exact science. Over time, monitor your rankings and user behavior. You may need to adjust your strategy, create new pages, or merge similar topics if certain pages don’t perform as expected.
Bonus Tip: Optimize Your Google Business Profile
Your Google Business Profile (GBP) isn’t just another online listing. It’s often the first place customers form an opinion about your business—before they even visit your website.
Here’s how a well-populated GBP looks:
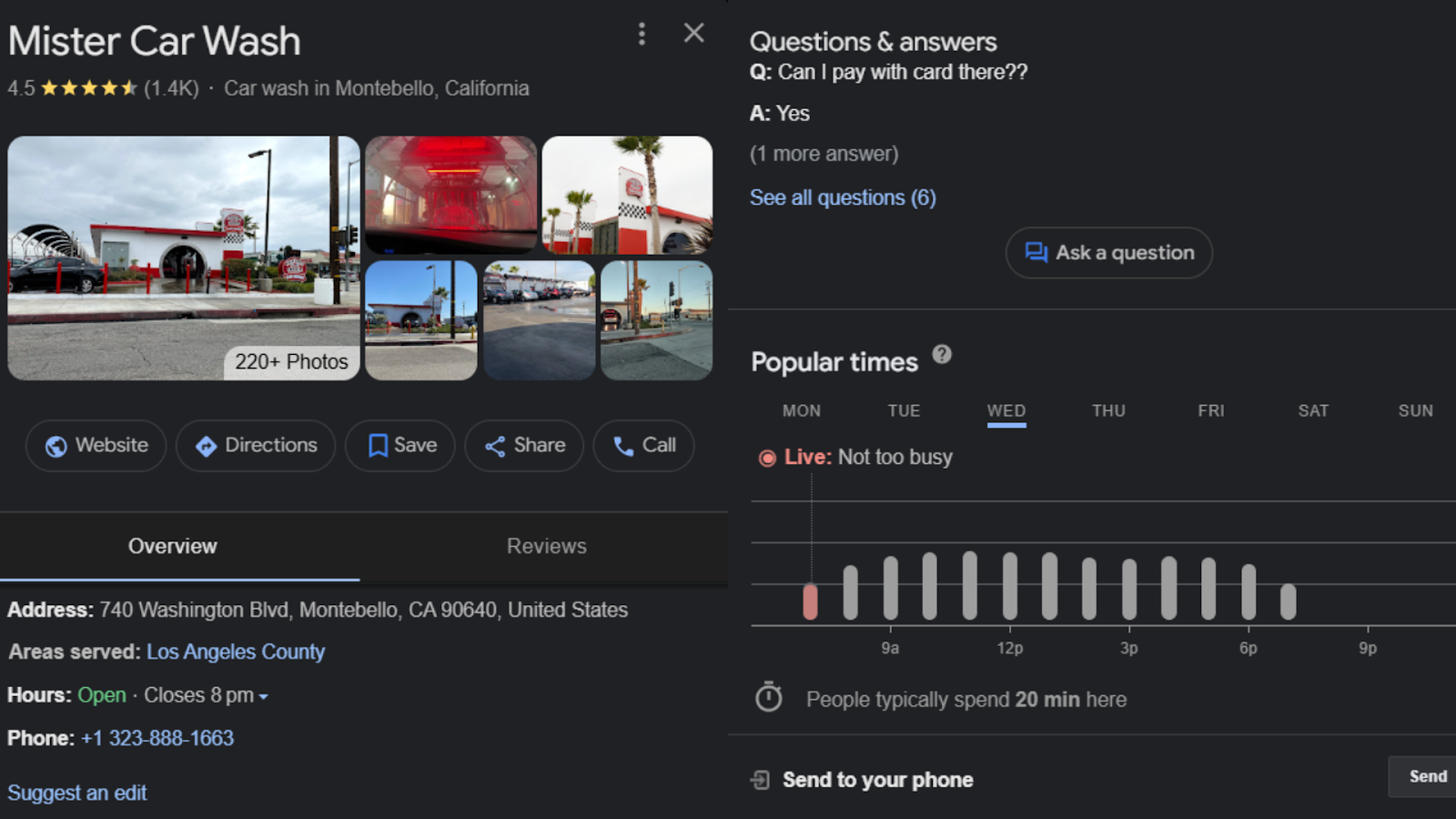
A well-optimized GBP can lead to more bookings, calls, and in-store visits. It shortens the decision cycle because customers find everything they need right there.
If your profile is incomplete, outdated, or missing key details, potential customers may assume you’re closed, unprofessional, or too hard to deal with. They’ll scroll right past you and choose a competitor. Don’t let that happen.
Here’s how to maintain your GBP:
- Officially claim your Google Business Profile and verify it. Without verification, Google may not trust the information you provide, and your business could appear less often in relevant searches.
- Add local keywords naturally to your business description. For example, if you’re a car wash in Bay Area, say Tire Cleaning in Bay Area rather than just “We clean tires.” This helps Google match your profile to local customers’ searches.
- Double-check your address, phone number, and website URL. Make them match what’s on your website and social media. Inconsistent info confuses customers and search engines—and can cause you to rank lower.
- Don’t upload a photo named IMG_123. Instead, rename it tire-cleaning-in-bay-area before uploading. Show off your storefront, products you sell, or team members. Good images build trust and encourage people to visit.
- Select categories that match what you actually offer. If you’re a car wash, say so. If you also offer auto repairs, add a related category. Don’t add irrelevant categories just for keywords—it’s against Google’s guidelines.
- Use your profile’s Updates feature to announce seasonal offers, new products, or upcoming events. Include local keywords where relevant. Regular updates show customers—and Google—that you’re active and reliable.
- Ask happy customers to leave reviews. When they do, thank them. If someone’s unhappy, respond politely and address the issue. Reviews aren’t just social proof—they contain keywords that can help boost your visibility.
- Highlight your business’s convenient features, like easy access for all vehicle types, free Wi-Fi in the waiting area, or a comfortable lounge for customers. Mention perks like contactless payment options and eco-friendly services to attract more attention.
- Answer common questions directly on your profile so customers don’t have to hunt for info. This keeps customers informed and engaged without extra effort.
And there you have it, a well-maintained Google Business Profile!
Get Your Small Business Going With the Right Keywords
In sum, local keyword research for small businesses starts with identifying core services and using them to find local, low competition + good volume keywords that match your target customers’ search intent.
Here are a few more guides to help you create a well-rounded local keyword strategy for any business:
↳ Keyword Research Checklist to Find Golden Keywords
↳ How to Get Local Keyword Search Volumes by City
↳ Free Keyword Research Template [With Guide]
↳ How to Do International Keyword Research
Frequently Asked Questions
SEMrush is one of the best tools for local keyword research. It helps you find local search terms, track rankings, and analyze competitors. Other great options include Ahrefs, Moz, and Google Keyword Planner. These tools show you what people in your area are searching for.
Start by listing what you sell and where you sell it. Then, use Google’s autocomplete, “People Also Ask,” and related searches to get keyword ideas. Check competitors’ websites and use tools like SEMrush or Google Keyword Planner to find high-ranking local keywords.
Local keyword research is finding search terms people use when looking for businesses in a specific area. For example, instead of “best pizza,” you’d target “best pizza in Chicago.” It helps businesses show up in local searches and attract nearby customers.
Use tools like SEMrush to see where your business ranks for local search terms. Just enter your keywords, set your location, and track changes over time. You can also check Google Search Console for search queries related to your site.
A local keyword includes a service or product plus a location. Examples: “best coffee shop in New York,” “affordable plumber in Dallas,” or “car wash near me.” These keywords help businesses attract local customers.
Think about what your business customers (not regular consumers) search for. Use Google, LinkedIn, and tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to find industry-specific terms. For example, instead of “marketing agency,” a B2B keyword would be “SEO services for law firms.”
Local SEO helps businesses show up in searches for their area. For example, a bakery in Miami wants to rank for “fresh bread in Miami.” By optimizing its website and Google Business Profile, it can appear when people search for local bakeries.
A local search happens when someone looks for a business near them. Examples: “best dentist in Brooklyn,” “hair salon near me,” or “pizza delivery in Chicago.” These searches usually bring up Google Maps results and local business listings.
Yes, you can do local SEO for free! You can optimize your Google Business Profile, add location-based keywords to your site, and get customer reviews. But if you want advanced tracking or keyword tools, you might need to pay for SEO software.
Use Google’s free tools like Keyword Planner and Google Trends. Type in a service you offer and check search suggestions. Look at the “People Also Ask” and “Related Searches” sections. Also, check what keywords your competitors use on their websites.
First, claim and update your Google Business Profile with accurate info. Then, add local keywords to your website and create location-based content. Get customer reviews, list your business in online directories, and make sure your contact details are the same everywhere.
